Conventional Magnetic Recording (CMR) or Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR)? Many people want to know the answer to this question when looking for the right hard drive for their use. This post from MiniTool introduces details about CMR vs SMR and you can know which one to choose.
Most people know that a hard disk drive (HDD) is a form of data storage that uses mechanical parts, not a solid-state drive (SSD) that uses flash memory. What people may not know is that different forms of magnetic recording take place in hard drives.
Both conventional magnetic recording (CMR) and shingled magnetic recording (SMR) are technologies used to physically store data on HDDs. Do you know the differences between them? Continue to read the following part.
CMR vs SMR
CMR vs SMR: Definition
What Is CMR
CMR refers to Conventional Magnetic Recording. It is also called PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording). CMR aligns the poles of a magnetic element perpendicular to the surface of the disk in a hard drive. Magnetic elements in this technology represent bits of data. Tracks are written side by side and do not overlap. Generally, the write head is larger than the read head, so manufacturers try to make the write head smaller in production.
What Is SMR
SMR refers to Shingled Magnetic Recording. With the continuous effort to achieve higher data density per square centimeter, SMR technology has also emerged to be able to manufacture higher and higher capacity hard drives with the same board count and size.
In this type of technology, a used read head is smaller than the write head, and the data tracks are stacked on top of each other. This increases the possibility of recording more data in the same area unit, that is to say, the density increases.
However, the problem is that tracks can be overwritten when trying to delete or modify stored data, which can lead to data corruption. The solution to this problem is to write all the data that needs to be modified into a single sector, which is responsible for reordering the data when there is a downtime in the use of the hard drive.
Tips:
Here are two other types of MR (magnetic recording).
- LMR (Longitudinal Magnetic Recording): It is a type of data storage that is stored longitudinally on the disk surface. The hard disk head will be able to magnetize this area one way or another (north-south orientation) to create 1s and 0s for binary information. This is the classic way of storing information on old hard drives.
- PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording): It has a distinct advantage over LMR because it is vertical, takes up less space per piece of data, and can store more information on the same disk surface. Also, it generates less heat by keeping the information in a more regular and stable area.
CMR vs SMR: Pros and Cons
CMR
Pros:
CMR hard drives are a good choice when you plan to store data at high transfer rates or store large amounts of data. This will include many different types of activities, from music streaming, audio, video, or image processing to use for NAS servers or general servers.
Cons:
CMR hard drives are more expensive than SMR drives.
SMR
Pros:
SMR drives are cheaper than CMR hard drives. SMR hard drives are a good choice if they are primarily used for data storage or PCs where large hard drives are used to store data. They offer more storage capacity and are more energy-efficient than CMRs, making them ideal for archiving tasks.
Cons:
Generally speaking, you can choose SMR if you want a large hard drive with a lower bill of materials cost and generally lower power consumption and only use it as a pure data storage device.
SMR hard drives are not particularly suitable if the drive is to perform writes continuously and permanently, as this could lead to buffer overflows. When you are constantly writing and rewriting data on the disk, large file transfer rates will be slow down.
CMR vs SMR: Brand
Below are typical brands of CMR and SMR.
Seagate: New Barracuda from 1TB to 8TB is usually SMR, while Ironwolf is usually a CMR hard drive.
Toshiba: Many of their 1TB to 6TB drives are usually SMR. Other products like X300, P300, and N300 are usually CMR.
Western Digital: Its variety is very diverse. The red series is a mix of SMRs and CMRs. Red Pro is CMR, blue is mixed, black is mostly CMR, and purple is CMR. Maybe you are interested in this post – Quick Guide: What do Western Digital Colors Stand for.
Related articles:
- Seagate vs Western Digital – What Are the Differences on Storage
- Seagate Barracuda VS WD Blue: Which One Should You Choose?
CMR vs SMR: Which One to Choose
Users should evaluate their storage and backup needs to determine the best drive for them. In principle, SMR drives will offer the same capacity as CMR drives at a lower cost per platter but offer less flexibility in usage.
SMR drives still offer random read capabilities for fast data access like CMR drives, but they are best suited for custom systems that take advantage of their high capacity and structure since they require ample idle time or continuous workloads for optimal performance.
SMR drives are recommended when they are used for backup and archival purposes, as infrequent drive access enables stable drive performance at a lower cost. Businesses looking to buy high-capacity drives also tend to favor SMR drives because they can provide the same capacity on fewer drives.
How to Back up Data to CMR or SMR Hard Drives
Whether you choose CMR or SMR hard drives, you may want to back up data to it. To do that, you can try MiniTool ShadowMaker. It is an excellent computer backup software, which is compatible with Windows 11, 10, 10, 8, 8.1, and 7. With it, you can back up files, folders, disks, partitions, and systems to an image file within a few clicks.
Now, download MiniTool ShadowMaker Trial Edition and install it on your computer to start a backup for data. Connect your hard drive to the computer.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Connect the hard drive to your computer. After downloading MiniTool ShadowMaker Trial Edition, double-click the .exe file and install it on your PC by following prompts on the screen. Please don’t install MiniTool ShadowMaker on your CMR or SMR hard drive.
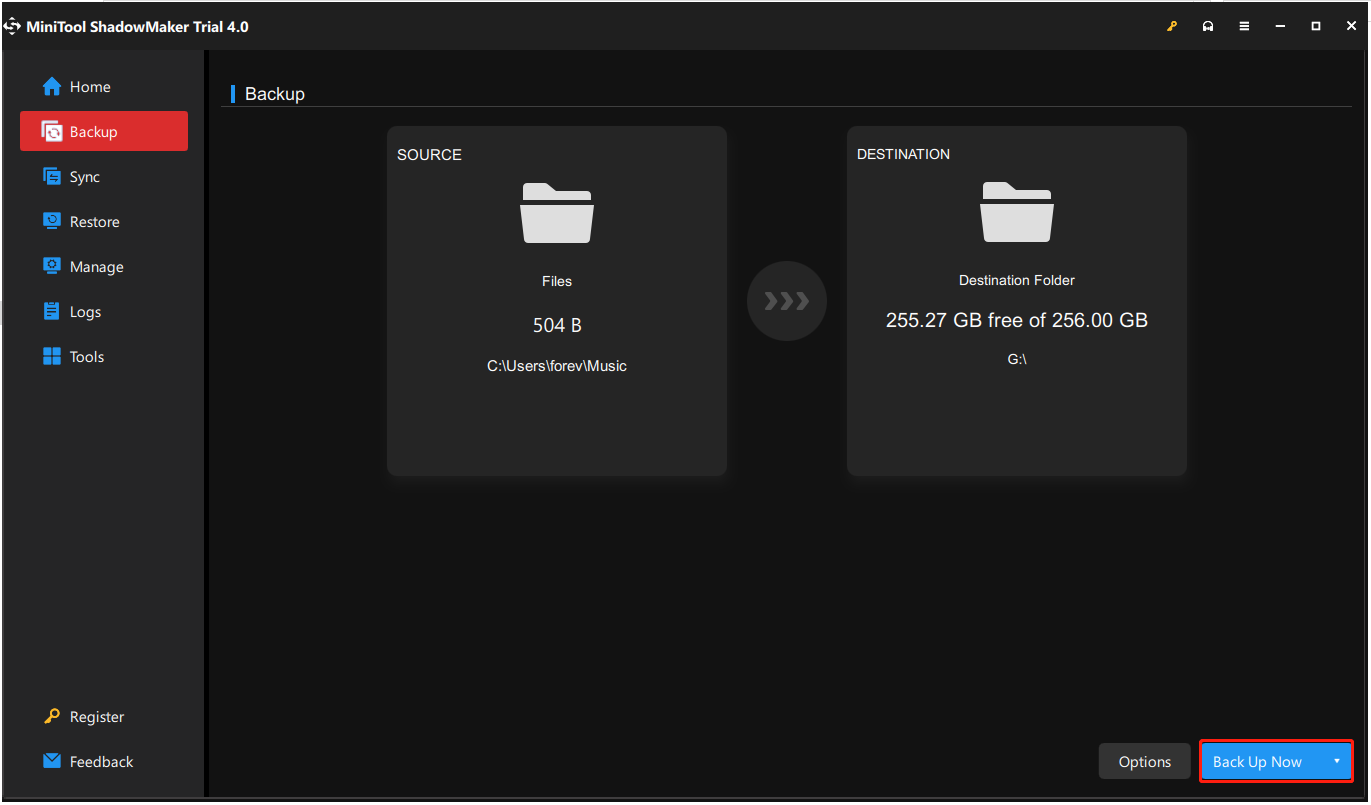
Step 2: Navigate to the Backup page. You may find this backup software backs up the system by default. To back up data, click SOURCE and choose Folders and Files. Then, check all the items that you want to back up and click OK.
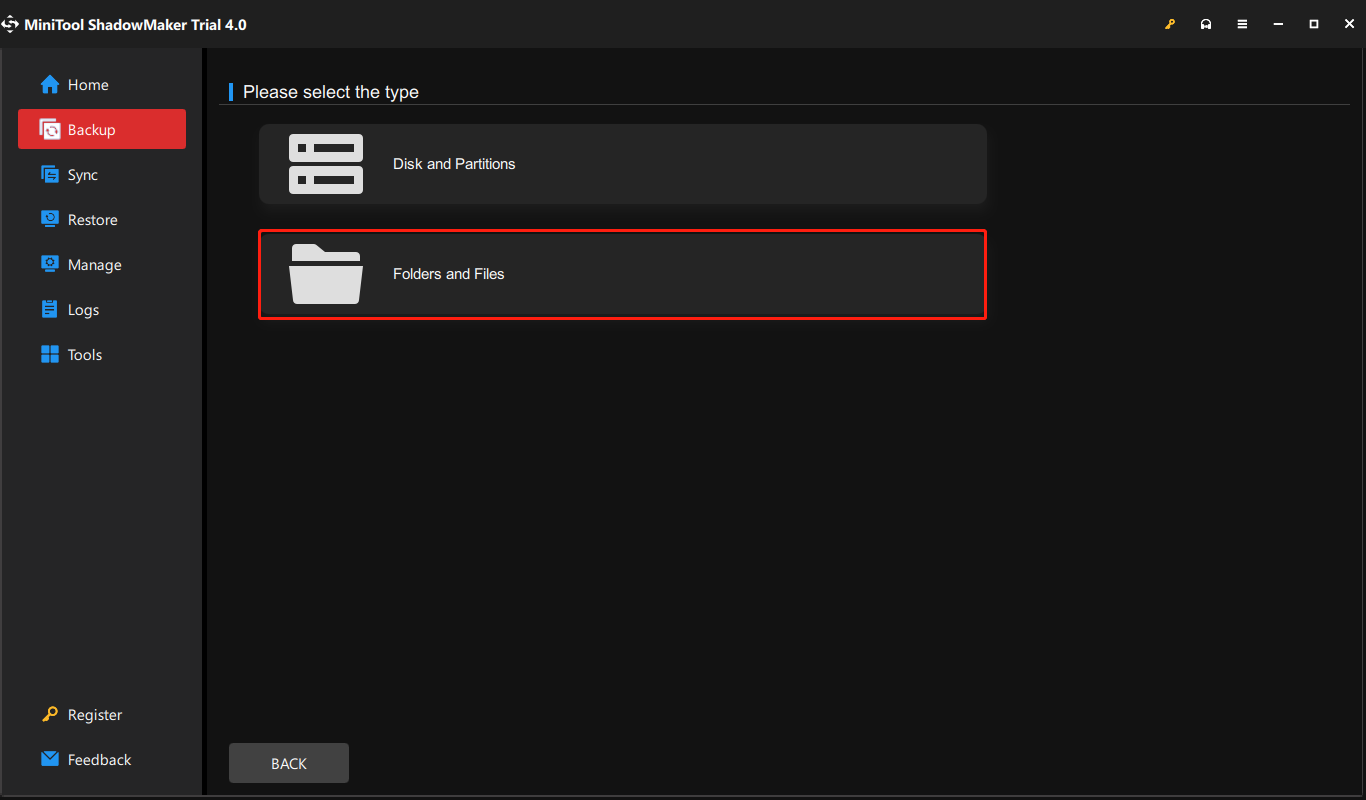
Step 3: Click the DESTINATION button, choose a destination to save your backup files, and then click OK. There are four destination paths for you – User, Computer, Libraries, and Shared. Here, you can choose your CMR or SMR hard drive as the destination.
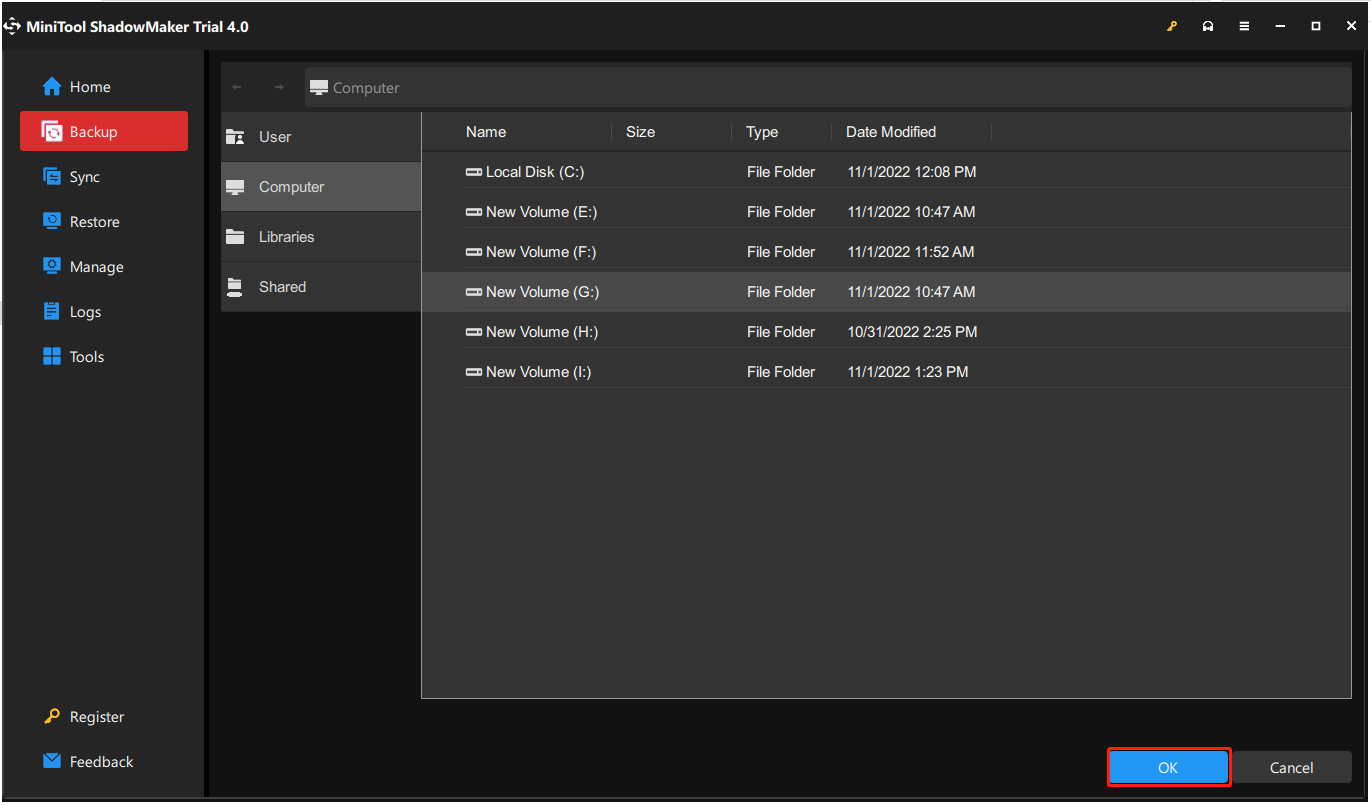
Besides, you had better make a scheduled plan for the backup. MiniTool ShadowMaker allows you to back up your computer daily, weekly, monthly, or on event. Click the Options > Schedule Settings button before clicking Back Up Now. Then, set the schedule and MiniTool ShadowMaker will start automatically backing up your data at a specific time.
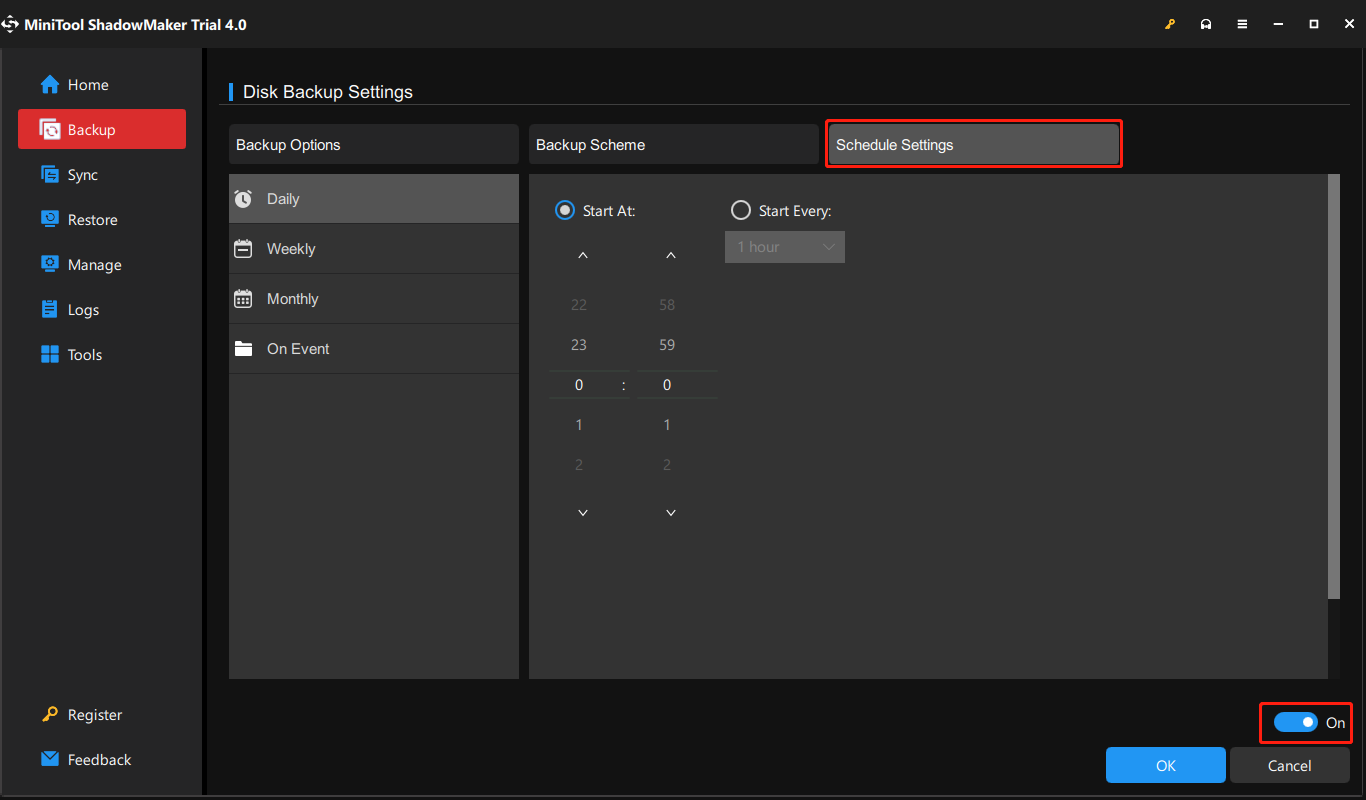
Minitool ShadoaMaker also allows you to create various backups, including full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups. If you want to do that, refer to this post – full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup. You can go to Options > Backup Scheme to set it.
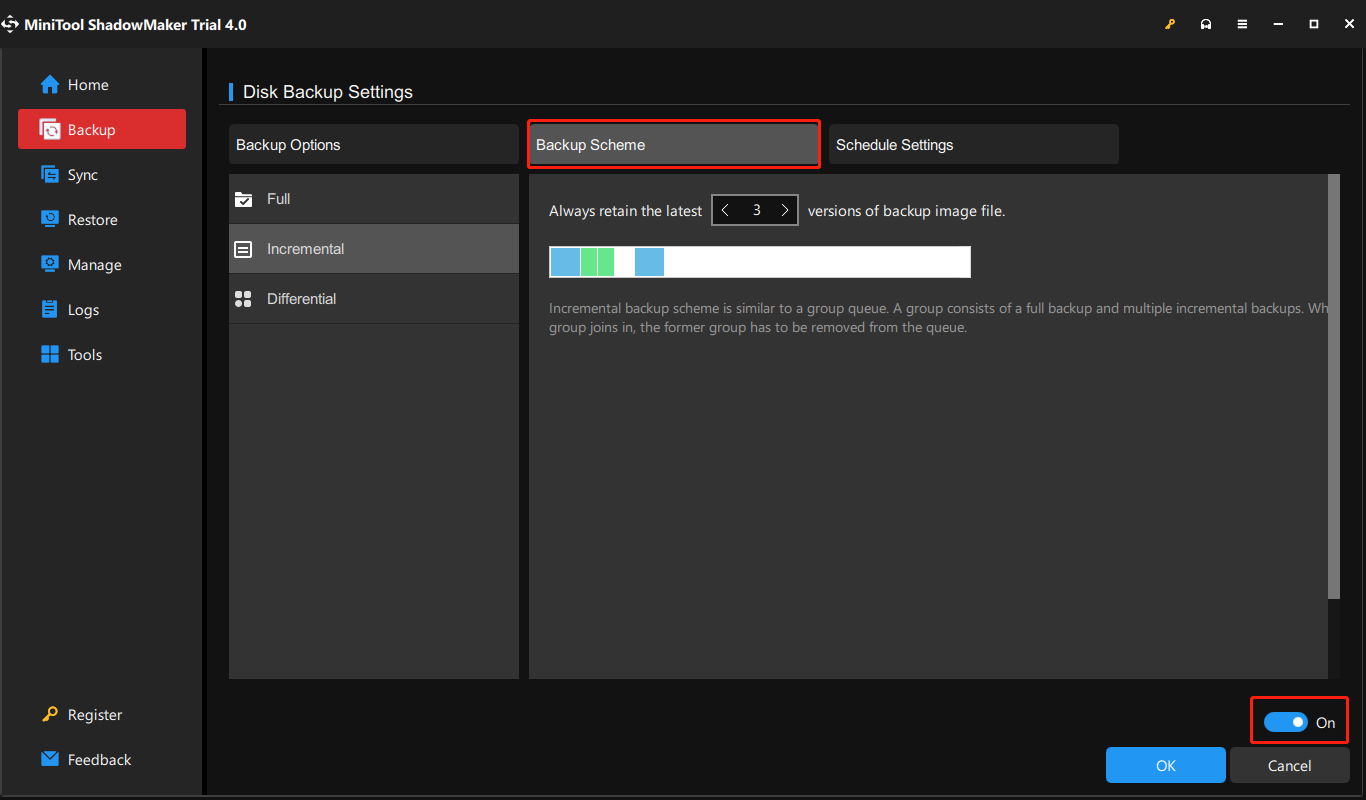
Step 4: At last, click the Back Up Now button to start the backup process.
How to Clone System to CMR or SMR Hard Drives
If you have gotten the CMR or SMR hard drives, you may want to transfer your system to the new hard drive. To migrate the system and files from an original hard drive to CMR or SMR hard drive without data loss, the clone tool is required. MiniTool ShadowMaker can also satisfy your demands.
To clone OS to the new hard drive, MiniTool ShadowMaker provides the Clone Disk feature. And now, we will show you how to migrate the operating system to CMR or SMR hard drive with MiniTool ShadowMaker.
Step 1: Download, install and Launch MiniTool ShadowMaker and click Keep Trial.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
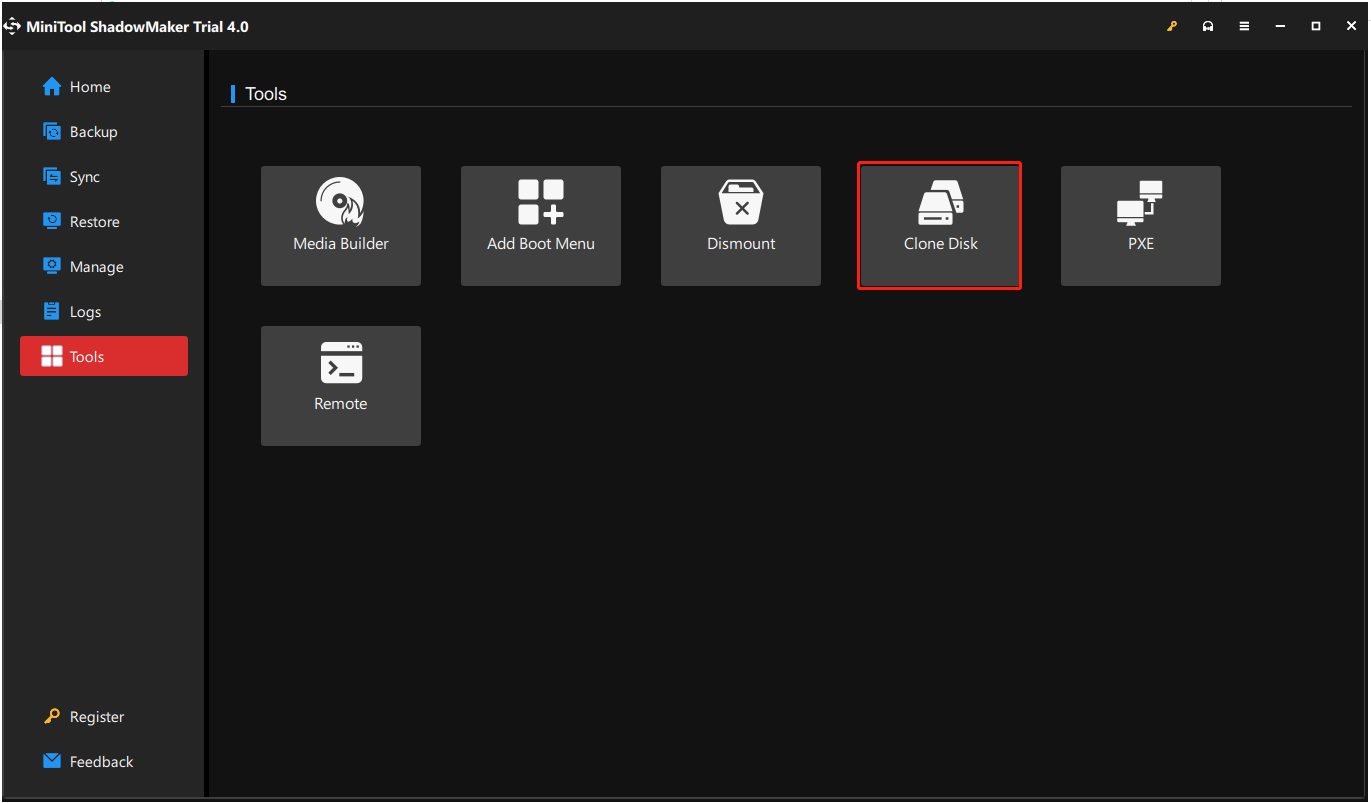
Step 2: Go to the Tools tab, and click the Clone Disk feature.
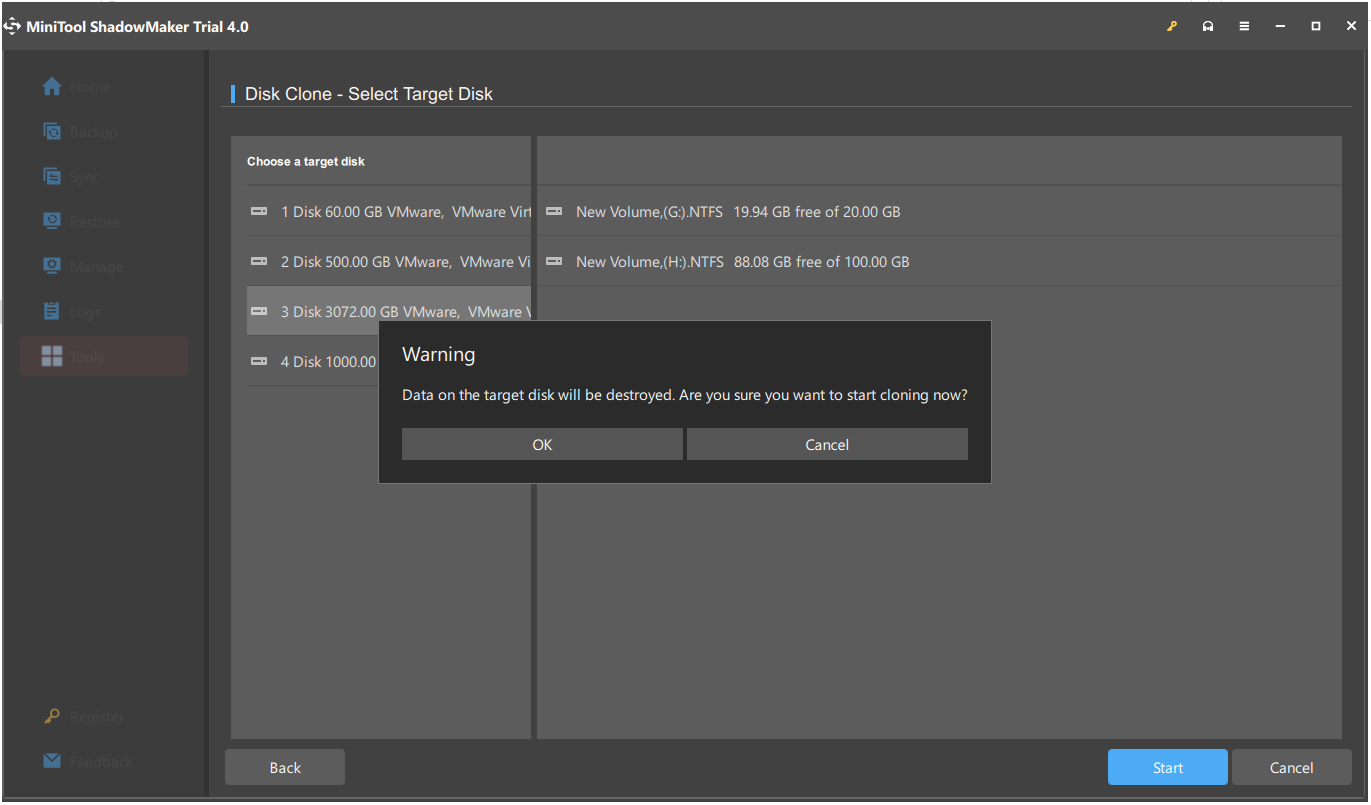
Step 3: In the new interface, choose a hard drive as the source disk – here you should choose the system disk. Besides, select the SMR or CMR hard drive as the target disk. When the “data on the target disk will be destroyed” message appears, click OK to ignore if your disk is empty or you have backed up files on it in advance.
Step 4: MiniTool ShadowMaker will start cloning the system disk to your new hard drive. After cloning, you will get the following information window.
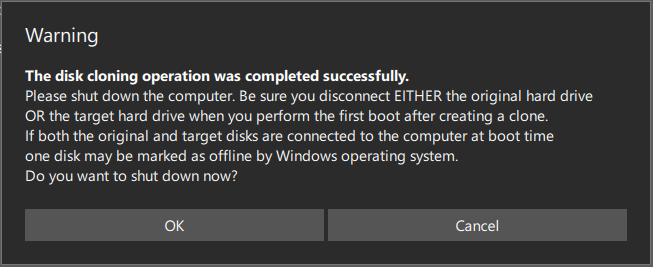
Due to the same disk signature, one disk is marked as offline. To boot your computer from the cloned hard drive, you should shut it down, open the case, remove the original disk, and put the new disk in the original place. If you clone a hard drive for backup, you can disconnect the target disk and put it in a safe location.
Bottom Line
Now, do you have a better understanding of CMR vs SMR? If you have different opinions on CMR vs SMR, please don’t hesitate to share them with us.
If you have encountered any issues when using MiniTool ShadowMaker, you can leave a message on the following comment zone and we will reply as soon as possible. If you need any help when using MiniTool software, you may contact us via [email protected].
User Comments :