What is MLC? What is TLC? What are the differences between MLC and TLC? As for MLC vs TLC, which one is the best for the storage application? This post from MiniTool will show you the answers.
SSD with a larger capacity has become increasingly popular because users have more and more files, such as photos, movies, games, etc. to store. When it comes to larger hard drive capacity, flash memory will be an important factor. Current SSD uses NAND flash.
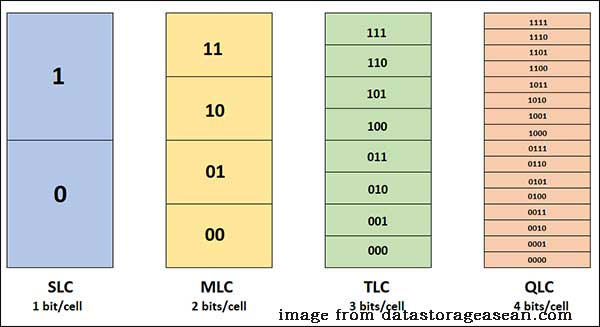
Different types of storage cells are used in flash memory. Units are classified according to the number of digits they can store. Some units can store one bit, while others can store multiple bits of data. The memory cells are divided into three types – MLC, TLC, SLC.
In the following part, we will show you some details about MLC vs TLC.
What Is MLC and TLC
MLC is the abbreviation of Multi-Level Cells and each cell of it can store two or more bits of data. It requires more complicated voltage control, with four variations of 00, 01, 10, and 11.
TLC, whose full name is the Triple-Level Cell, stores three bits of information per cell. Its voltage has 8 changes from 000 to 111. Besides, TLC is the most common type of SSD.
Now, let’s talk about the differences between MLC and TLC.
MLC VS TLC
MLC VS TLC: Performance
As for the performance of QLC and TLC SSD, we will give you a brief introduction. The performance of an SSD depends on its flash memory unit. An SSD with a three-bit data unit will be slower because there are more bits to read. Compared with MLC SSD, read and write operations of TLC SSD will take more time.
So, MLC has better performance than TLC.
Also see: How to Get Best Performance from SSD in Windows 10/8/8.1/7
MLC VS TLC: Durability
In addition to performance, endurance is also an essential factor for an SSD. Thus, this part is about TLC vs MLC for durability. Compared with a cell that stores three bits of data, a cell that stores only one bit will be written fewer times. The fewer the number of writes on a cell, the longer its lifespan.
The read/write life cycle of TLC is short, with only 1,000 to 3,000 cycles per unit, while the data read/write lifespan of MLC is longer, each unit is about 3,000 to 5,000. TLC will be more expressive than the full capacity of SLC and MLC drives but at the expense of relative durability.
Thus, the durability of TLC is lower than the MLC.
MLC VS TLC: Speed
Apart from the performance and endurance of MLC vs SLC SSD, speed would be another essential factor.
If the SSDs on the TLC and MLC are connected through the SATA-3 protocol, they are likely to show the same speed, especially when it comes to fairly cheap solid-state memory. However, if the TLC drive is connected to the system unit through the PCIe NVMe interface, it can run faster than the MLC memory type SSD through PCIe.
Thus, MLC vs TLC: speed depends on whether they are connected with SATA-3 or PCIe.
MLC VS TLC: Power Consumption
Then, the next aspect of MLC vs TLC NAND is power consumption.
When both TLC and MLC memory is connected through the SATA-3 protocol, they will consume approximately the same amount of energy. However, if you connect TLC memory via SATA-3 and MLC memory via PCIe, you will find that TLC SSD consumes several times less energy (up to ten times).
MLC VS TLC: Price
When choosing an SSD, the budget would also be taken into consideration. The cost of an SSD depends on its unit type. SSDs that store one bit of data in a cell will be more costly than densely packed SSDs since they can store two or more bits of data. So in most cases, MLC SSDs are more expensive than TLC SSDs.
As for MLC vs TLC of price, MLC is more expensive than TLC.
MLC VS TLC: Which One to Choose
It is important to evaluate what type of flash memory your system needs. Then, you may wonder which one to choose. The following are some of our suggestions.
MLC is a great choice since it is the best combination of performance, speed and reliability. At the same time, it is within the budget of most consumers. Besides, MLC SSD is an ideal choice for users of servers, disk-intensive applications such as video editing software, and mainstream consumers who want maximum performance from the system.
TCL aims to provide low-cost options for users who need low-cost high-capacity SSDs. Users who perform daily tasks on the device but need to improve the performance of their laptops and desktops can consider using TLC SSDs. TLC SSDs are also ideal for users who want to store media files on SSDs.
To sum up, if speed and price are essential for your system, TLC is appropriate. If performance and endurance are essential, MLC is recommended.
How to Upgrade to Large SSD?
Since SSD has better performance than your original hard drive. So, some people ask whether there is a way to upgrade the original hard drive to the larger SSD without data loss. Of course, the answer is positive. In the following part, we will show you how to upgrade the hard drive to a large MLC SSD or TLC SSD.
To upgrade the hard drive to a large MLC or TLC SSD, you can use a hard drive clone tool. Thus, MiniTool ShadowMaker, which is also a piece of Windows 10 backup software, would be a good choice. MiniTool ShadowMaker enables you to clone OS to SSD without data loss. Thus, you can use it to clone your hard drive to the MLC or TLC SSD.
Now, follow the guide below to migrate your operating system to SSD with MiniTool ShadowMaker’s Clone Disk feature.
Step 1: Insert the SSD to your computer. If there is no extra disk card slot on the motherboard, you can only use a cable to connect the SSD to the computer. Install and launch MiniTool ShadowMaker. Please don’t install the program on your SSD.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2: Launch it to get into the main interface.
Step 3: Go to the Tools page and then click the Clone Disk feature.
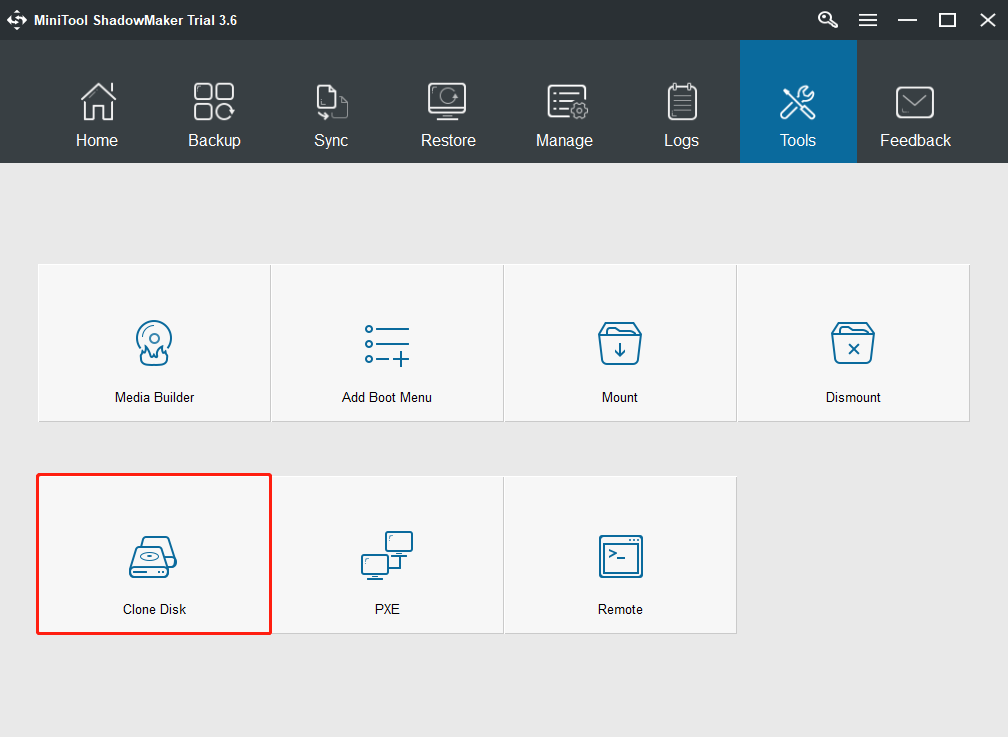
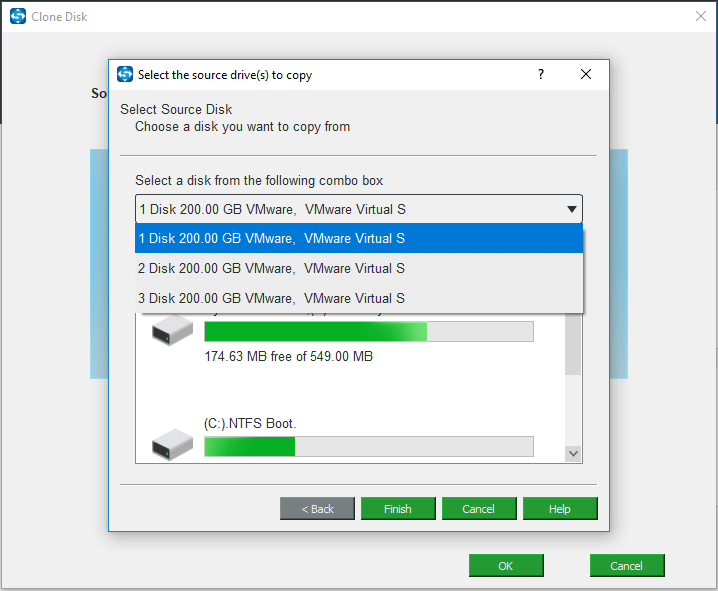
Step 4: Then, click Source to choose the source disk. Here, you need to choose the original system disk as the clone source and click Finish to continue.
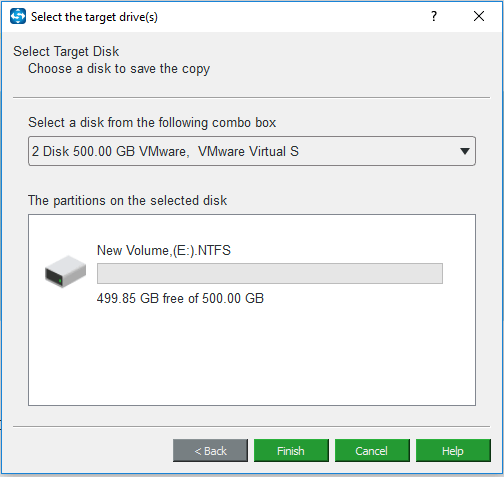
Step 5: Then click the Destination module to choose a target disk. Here, you need to select the MLC or TLC SSD as the target disk.
Step 6: Then the disk clone process will begin. Please do not interrupt the disk clone process until it is finished. The costing time depends on the number of files on the source disk.
Step 7: When the disk clone process is finished, you will receive a warning message which tells you that the target disk and the original disk have the same signature. So, you need to remove or disconnect either of them. Moreover, if you want to boot the computer from the target disk, please enter BIOS and change the boot sequence first.
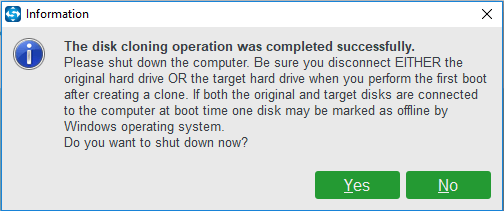
After all steps are finished, you have successfully upgraded the original hard drive to the MLC or TLC disk.
In addition, if you only want to migrate Windows OS from HDD to SSD, you can try another hard drive cloning software – MiniTool Partition Wizard. It offers you the Migrate OS to SSD/HD feature, enabling you to only migrate Windows system to SSD or clone the entire system disk to SSD.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Related article: Easily Migrate Windows 10 to SSD without Reinstalling OS Now!
Further reading: SSD VS HDD
Digital data is stored in a binary form called bits, which is just a sequence of 0 and 1. HDD uses magnetic platters to store data. Each platter is divided into billions of tiny areas that can be magnetized and demagnetized. The magnetized area represents 1, and the demagnetized area represents 0.
On the other hand, SSDs use cell (NAND) flash memory to store data instead of magnetic disks. When a cell is charged, it represents 1 and when it is discharged, it represents 0. Data is accessed electronically from the unit in the flash memory while reading and writing data on the disc requires a mechanical process. It makes SSD faster than HDD.
If you want to learn more information about SSD vs HDD, please refer to this post – SSD VS HDD: What’s Difference? Which One Should You Use in PC.
Bottom Line
To sum up, this post has introduced information about MLC vs TLC. If you do not know the differences between them and do not know which one is better, the above content may help you.
In addition, if you have any different ideas of MLC vs TLC, you can share them in the comment zone, or please feel free to contact us via email [email protected] and we will reply to you as soon as possible.

User Comments :