Before comparing the differences between recovery time objective and recovery point objective, let’s learn some related background knowledge of them.
Disaster Recovery (DR) and IT Service Continuity (ITSC)
What Is Disaster Recovery?
Disaster recovery refers to a set of policies, tools, as well as procedures to enable the recovery or continuation of crucial technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster.
Disaster recovery focuses on the information technology (IT) or technology systems that support vital business functions. Being opposite to business continuity (BC), DR involves keeping all essential aspects of a business functioning despite significant disruptive events.
Therefore, disaster recovery can be regarded as a subset of business continuity. It assumes that the primary site is unrecoverable, at least for some time, and represents a process of recovering data and services to a secondary survived site. That is opposite to the process of restoring back to its original location.
What Is IT Service Continuity?
IT service continuity is a subset of business continuity planning (BCP) and includes IT disaster recovery planning & wider IT resilience planning. It also incorporates those elements of IT infrastructure and services that relate to communications like data communications and telephony/voice.
The IT service continuity plan reflects the recovery point objective (recent transactions) and recovery time objective (time intervals), which have been defined by Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL). ITIL is a set of detailed practices for IT activities like IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of businesses.
Now, let’s compare these two simple terms and figure out their differences.
1. RPO vs RTO: Definition
RTO vs RPO refers to recovery time objective vs recovery point objective.
What Is Recovery Point Objective?
RPO recovery point objective is the maximum targeted period in which data (transactions) might be lost from an IT service due to a major incident. It is defined by business continuity planning.
If the disaster recovery point objective is measured in minutes or even a few hours, then in practice, off-site mirrored backups must be continuously maintained since a daily off-site backup on tape won’t suffice.
What Is Recovery Time Objective?
RTO recovery time objective is the targeted duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster or disruption to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity.
In accepted business continuity planning methodology, the disaster recovery time objective is established during the business impact analysis (BIA) by the owner of a process. The establishment of RTO also includes identifying options time frames for alternate or manual workarounds.
2. RPO vs. RTO: Relationship
A recovery that isn’t instantaneous will restore transactions (data) over a period of time. By doing this, it won’t incur significant losses or risks.
The recovery point objective measures the maximum time period in which recent data might have been permanently lost in the event of a major incident. Yet, RPO isn’t a direct measurement of the quantity of such loss.
For example, if the business continuity plan is “restore up to last available backup”, then the recovery point objective is the maximum interval between such backup that has been safely vaulted off-site.
Instead of an existent backup regime, the recovery point objective is determined by business impact analysis. When any level of off-site data preparation is required, the period during which data might be lost often starts near the time of the beginning of the work to prepare backups instead of the time the backups are taken off-site.
In a large amount of literature on the recovery time objective, RTO is treated as a complement of the recovery point objective. Both RTO and RPO describe the limits of acceptable or tolerable IT service continuity performance in terms of time lost (RTO) from normal business process functioning and data lost or not backed up during that period (RPO) respectively.
Although both recovery point objective and recovery time objective are similar in measurement metrics, they still differ in some aspects.
3. RTO vs. RPO: Influence for Computer System Design
Both recovery point objective and recovery time objective must be balanced, taking business risk into account, and along with all the other major system design criteria.
The recovery point objective is tied to the time backups are sent offsite. Off-siting via synchronous copies to an offsite mirror allows for most unforeseen difficulty. The use of physical transportation for tapes or other transportable media comfortably covers some backup needs at a relatively low cost.
Recovery can be enacted at a predetermined site. Shared off-site space and hardware complete the package needed. For high volumes of high-value transaction data, the hardware can be split across two or more sites and split across geographic areas adds resiliency.
4. RPO vs RTO Disaster Recovery: Data Priority
The recovery point objective focuses on the amount of data that is lost due to a failure event. Instead of production downtime, RPO calculates the effect and risk to overall customer transaction whereas the recovery time objective only cares about application and system restoration.
5. Disaster Recovery RTO vs RPO: Application
The purpose of the recovery time objective is to deal in time to restore and inform the development of a disaster recovery strategy. While the recovery point objective handles data loss and informs the development of a backup strategy.
6. Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) vs Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): Cost
The expenses are different between both objectives. The costs for maintaining a granular recovery point objective may be smaller than those of a demanding recovery time objective. It is because RTO management involves the whole business infrastructure not just the element of data maintaining to RPO.
7. RTO Versus RPO: Calculation Variables
Based on the least number of variables, recovery point objectives can be easier to calculate thanks to the consistency of data usage. Yet, recovery time objectives are a little bit more difficult for restoration times rely on several factors including analog time frames and the day of which the event occurs.
A shorter recovery point objective means losing less data, but it needs more backups, more storage space, as well as more computing and network resources for backups to run. Thus, a shorter RPO costs more money.
Calculation variables may also differ according to the classification of data. For any company, a good practice is to sort data into critical and noncritical types. Then, that will predetermine your RTOs and RPOs in priority order.
8. RPO Versus RTO: Automation
Recovery point objectives just require you to carry out data backups at the right intervals. Then, data backups can be easily automated and implemented. Yet, this is virtually impossible for recovery time objectives since they involve restoring all IT operations.
Reduce RTO and RPO with MiniTool Disaster Recovery Solutions
As one of the many disaster recovery companies, MiniTool provides disaster recovery services to its customers with three disaster recovery products: MiniTool ShadowMaker, MiniTool Partition Wizard, and MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
Solution 1. MiniTool ShadowMaker
MiniTool ShadowMaker is a professional and reliable data backup tool that enables you to back up various kinds of data including documents (word, excel, txt, ppt, pdf, note, etc.), media files (photos, pictures, screenshots, images, graphics, audios, music, videos, movies, etc.), emails, programs/software, operating system, and so on.
The following is an example guide of backing up files with MiniTool ShadowMaker.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Download, install, and launch MiniTool ShadowMaker on your computer.
2. If it asks you for purchase, just click Keep Trial on the upper right of the screen.
3. When it enters its main user interface (UI), on the top menu, click the Backup tab.
4. It will shift to the Backup screen, there, click the Source module in the left to select the files you want to back up.
5. In the right of the Backup tab, click the Destination module to choose a destination to save the backup image. An off-site storage device is preferred.
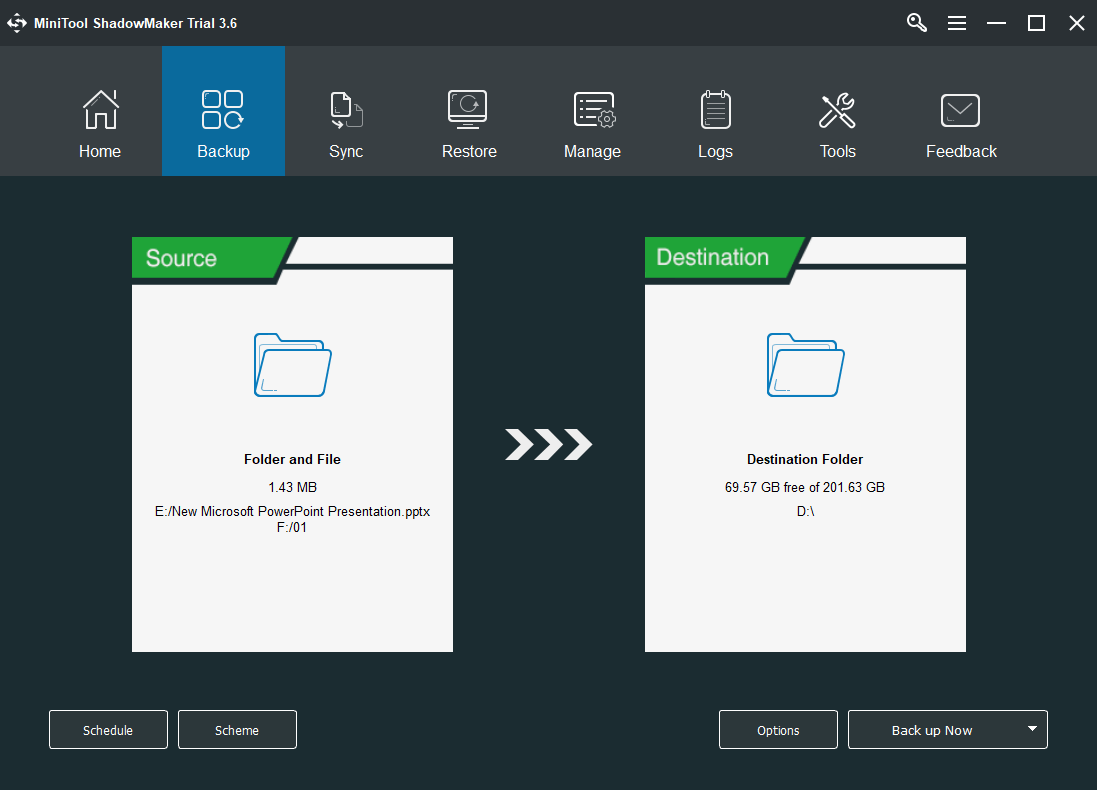
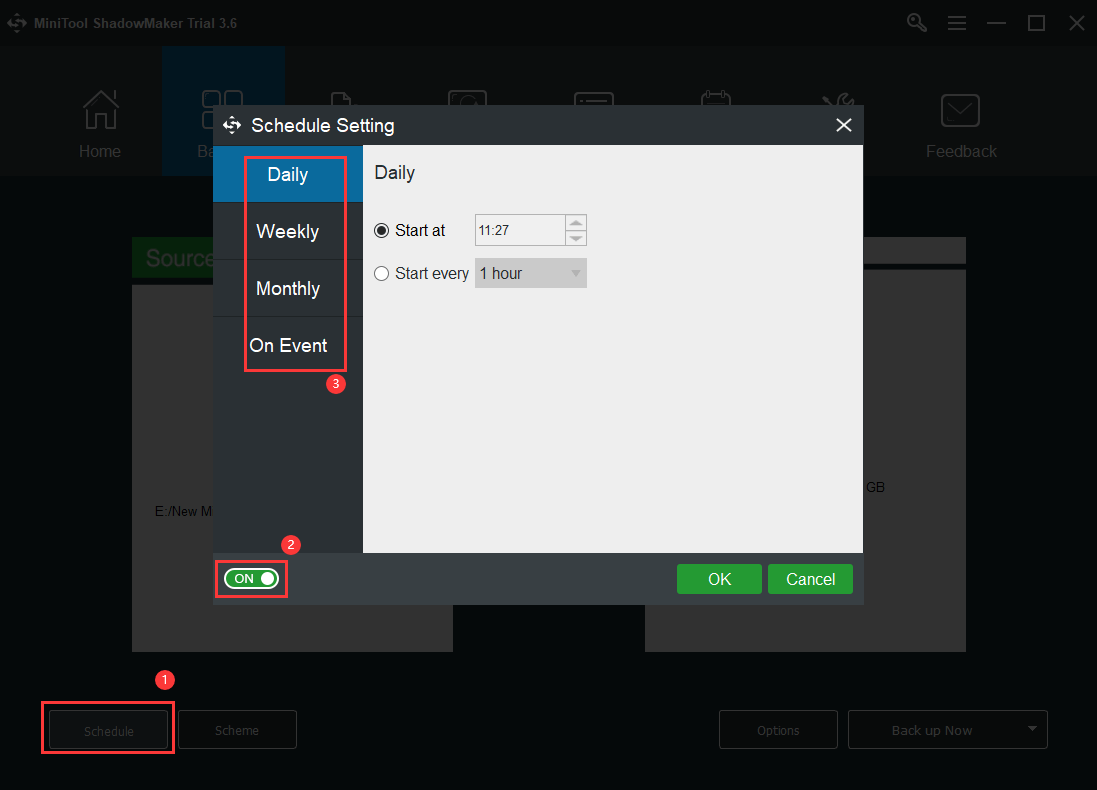
6. To perform file backup automatically in the future, you need to set up a schedule for this task. Click the Schedule button in the bottom left corner, switch on schedule settings, and specify a recovery point objective that suits you most, daily backup, weekly backup, monthly backup, or on-event backup.
7. When all settings are done, finally you can click the Back up Now button to start the backup process.
Solution 2. MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a powerful and well-known disk partition management tool, which also allows you to recover lost data with its Data Recovery feature. Just refer to the following instruction to restore your lost data.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Download, install, and open MiniTool Partition Wizard on your PC.
2. Connect the device, from where you’d like to recover data, to the PC.
3. On its main UI, click Data Recovery on the top left.
4. In the Data Recovery window, select the target location to scan for the lost data.
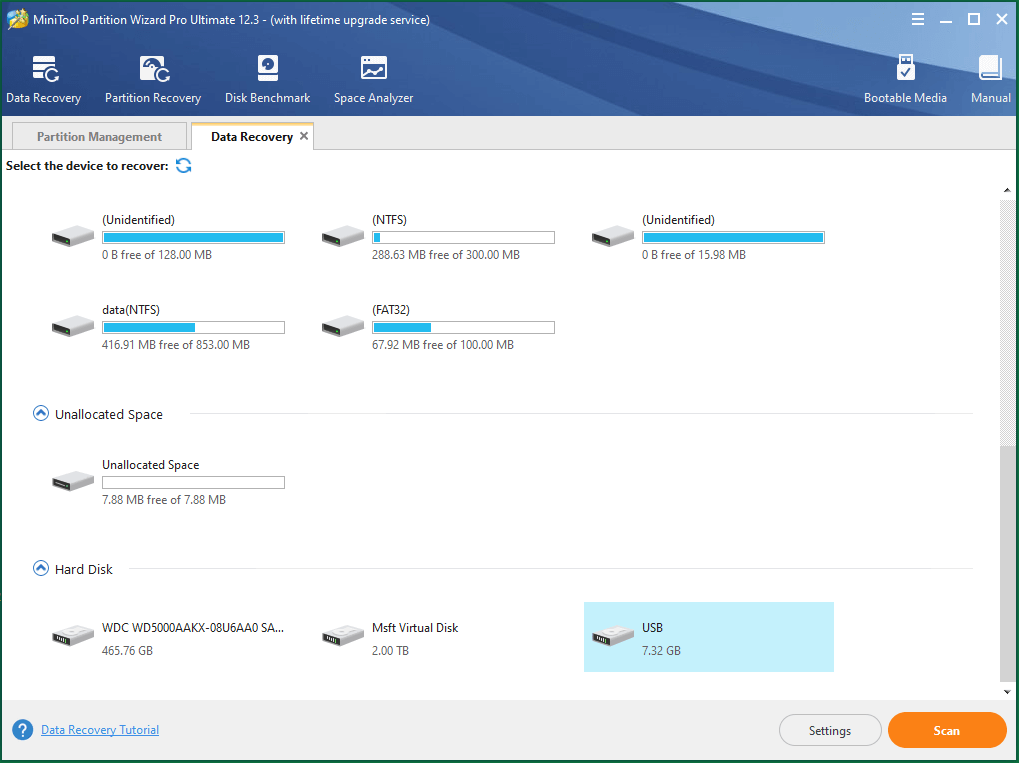
5. When it finishes scanning the target location, it will list all the lost items ever in the location. You can preview most of the lost documents to help you decide whether they are the ones you want to recover.
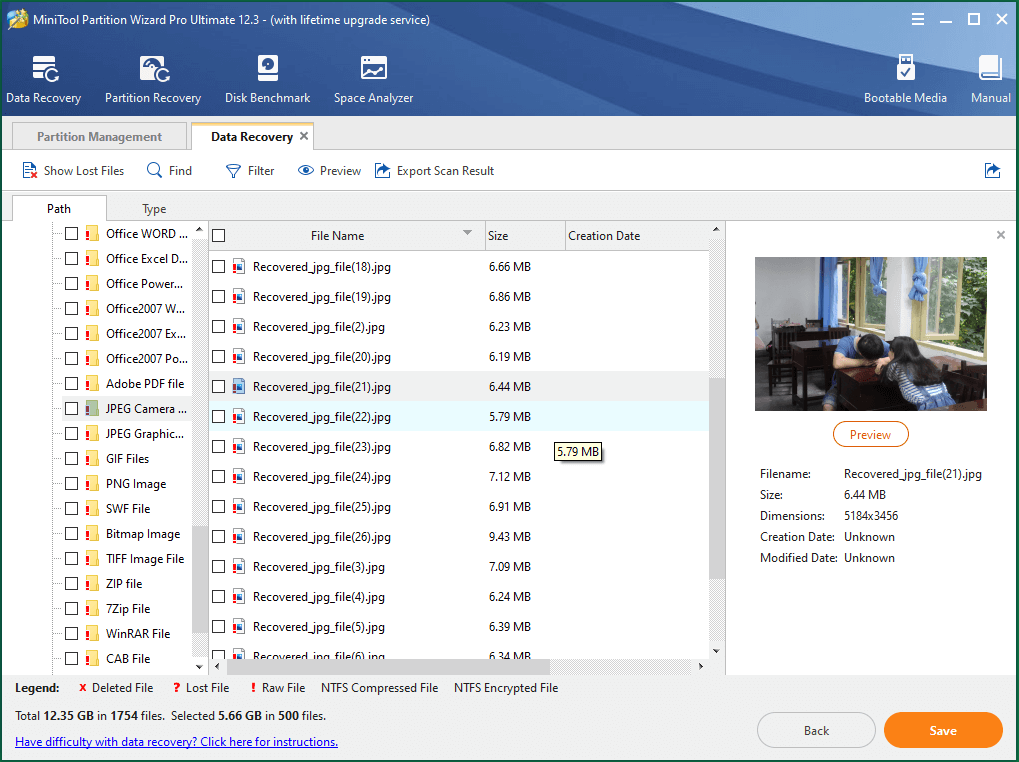
6. Select the files you’d like to restore from the scanned result, choose a location to store the recovered files, and click the Save button to start the process.
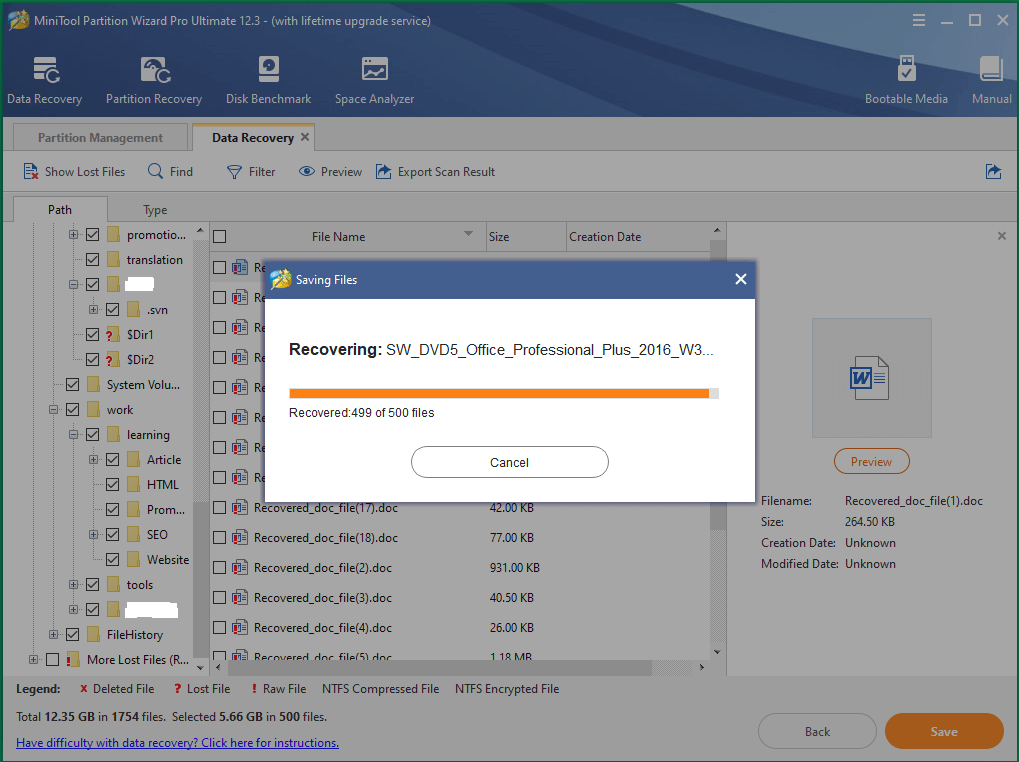
When the restoration finishes, just go to the location where you pick up to save recovered files. You will find your lost files are there!
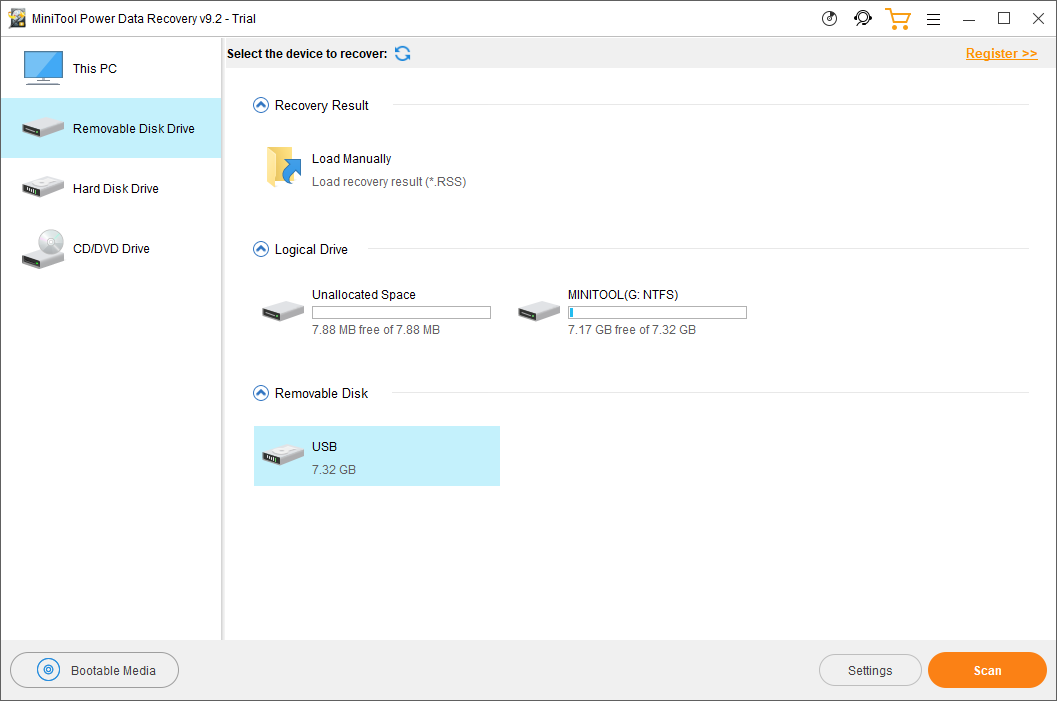
Solution 3. MiniTool Power Data Recovery
MiniTool Power Data Recovery is a robust and effective disaster recovery software that can help you restore data lost through deleting, formatting, wiping/erasing, or system crash. It is able to recover documents, media files, emails, programs/software, etc. from internal HDDs/SSDs, external hard drives, removable disk (e.g. USB flash drive, memory card, SD cards), CDs/DVDs…
MiniTool Power Data Recovery TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
The steps for data disaster recovery by MiniTool Power Data Recovery are very similar to those of MiniTool Partition Wizard. Just refer to the above guide if you choose to make use of this program.
Conclusion
Finally, let’s recall all the differences between recovery time objective and recovery point objective: definition, effects to computer system design, priority, cost, calculation variables, and automation. If you have any different ideas about RTO vs RPO, feel free to leave a comment in the below section.
Also, we have introduced you with 3 disaster recovery solutions offered by MiniTool. If you encounter any problem while using any one of them, their email support service ([email protected]) have you covered.


User Comments :