What Is Search Indexing?
In relational databases, an index is a single, physical storage structure that sorts the values in one or more columns of a database table. It is a collection of values in one or more columns of a table and a corresponding list of logical Pointers to the data page in the table that physically identifies those values.
When there are a large number of data, the first method of searching for information is a full table search that takes out all the records one by one, compares them with the query conditions, and returns the records that meet the conditions, which consumes a large amount of system time and causes a large number of disk I/O operations.
The second method is to create an index in the table, then find the index value that matches the query criteria in the index, and finally find the corresponding record in the table through the ROWID (equivalent to the page number) saved in the index.
With the help of search indexing, you can get the most valid and up-to-date results in seconds; otherwise, the searching process could take minutes, for the same operation to complete.
But at the same time, search indexing has some cons you may pay attention to:
1. The indexing process can take up available space if there are lots of files that are small in size. The index size will increase dramatically in proportion to the size of the files.
2. When the data in the table is added, deleted, and modified, the index also needs to be maintained dynamically, which reduces the speed of data maintenance.
Related article: [Solved] File Explorer Search Not Working in Windows 10
What Does It Mean If the Index Is Not Running?
Since indexing is related to search, when you encounter the indexing not running issue, you may find your search may take 10x more time as compared to indexing or directly fail to run.
The reasons behind this are complicated. That may be triggered by some search issues, slight application configuration errors, or corruption of Windows installation files in your computer.
To target these issues, you can follow the next methods and your Windows indexing issue will be resolved.
Fix: Windows 10 Indexing Is Not Running
Fix 1: Rebuild the Index Forcefully
Before you start other methods, it is possible that the indexing might be working but its options might be broken. In that situation, the fixes will be much easier. You can try to rebuild the index forcefully first by following the next steps.
Step 1: Press the Window key to open the Start menu and after clicking on Settings, go to Search.
Step 2: In the Searching Windows tab, scroll down from the right panel and click Advanced Search Indexer Settings under More Search Indexer Settings.
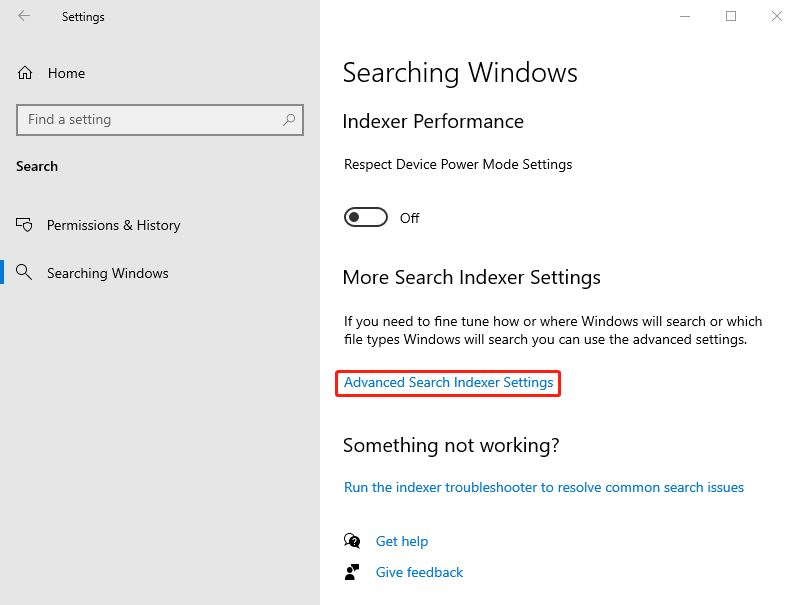
Step 3: In the pop-up window, click on Advanced present at the bottom of the window.
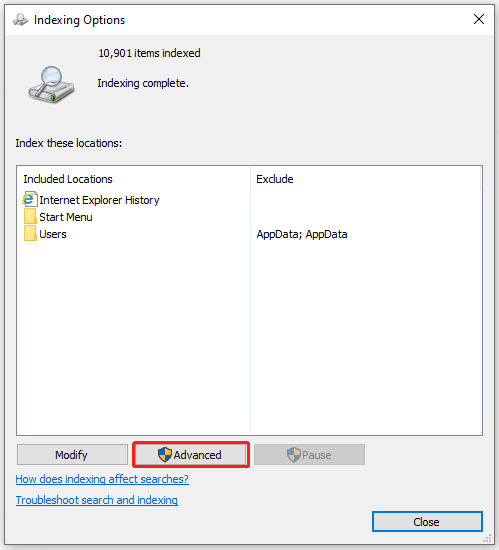
Step 4: Under the Troubleshooting tab, click on the option of Rebuild. Then click OK to confirm.
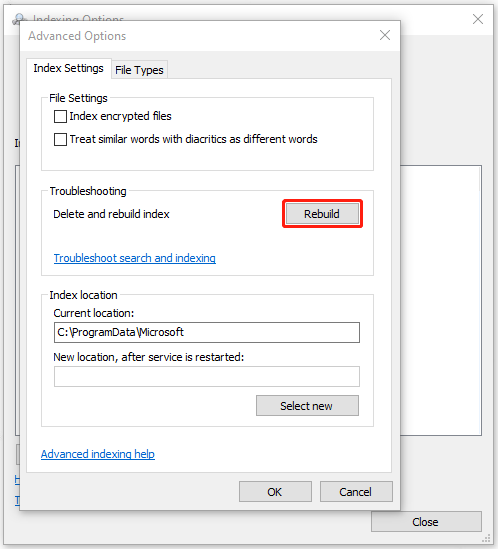
The process will take some time. When it finishes, you can check if the Windows indexing issue is fixed.
Fix 2: Check Windows Search Status
Windows search service is used to manage search operations. You need to make sure the service run well on your computer or that will affect the normal operation of indexing, resulting in the indexing service missing in Windows 10.
Step 1: Open the Run dialogue box by pressing Windows + R and type services.msc to enter.
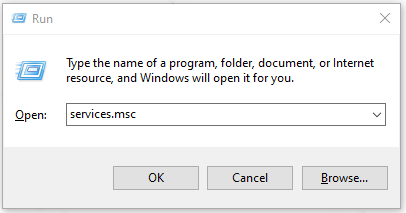
Step 2: Then scroll down to locate Windows Search. Right-click on it and choose Properties.
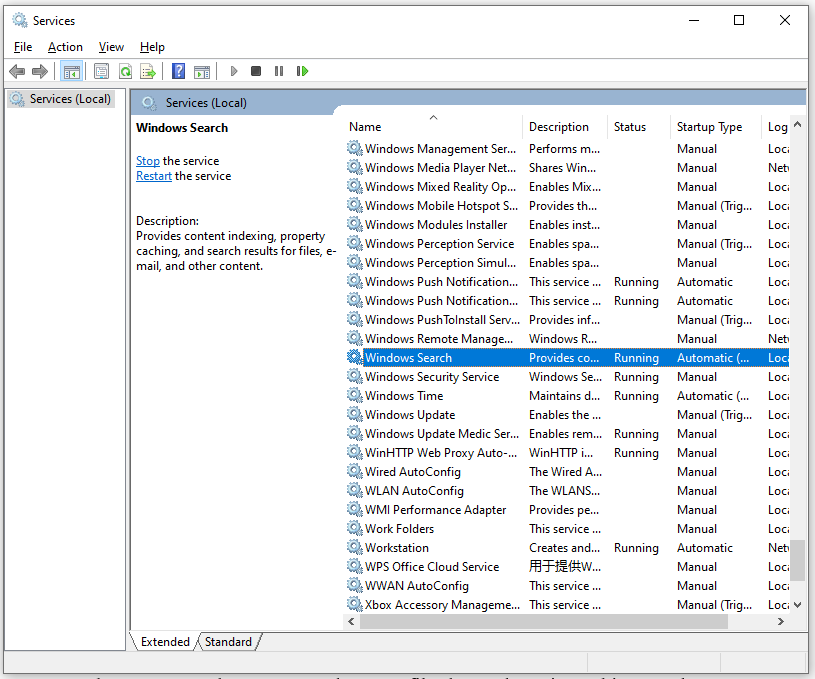
Step 3: In the pop-up window, choose the startup type as Automatic. If the service is disabled, please click on Start and then choose Apply to save your changes.
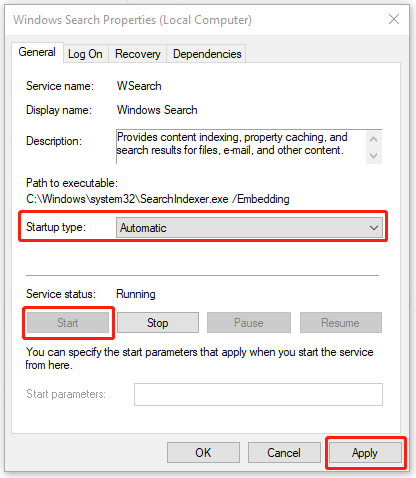
Note: If the service status is running, you can stop it first and click Start to restart it.
Restart your computer completely and check if the problem that the search indexer stops working has been solved.
Fix 3: Disable Cortana
As examined by some users, disabling Cortana may be a useful fix. Cortana is a virtual assistant integrated with Windows search It is worthwhile disabling Cortana-enabled indexing.
Step 1: Open Settings in Start and go to Apps.
Step 2: Scroll down from the right panel and click on Cortana and then Advanced options.
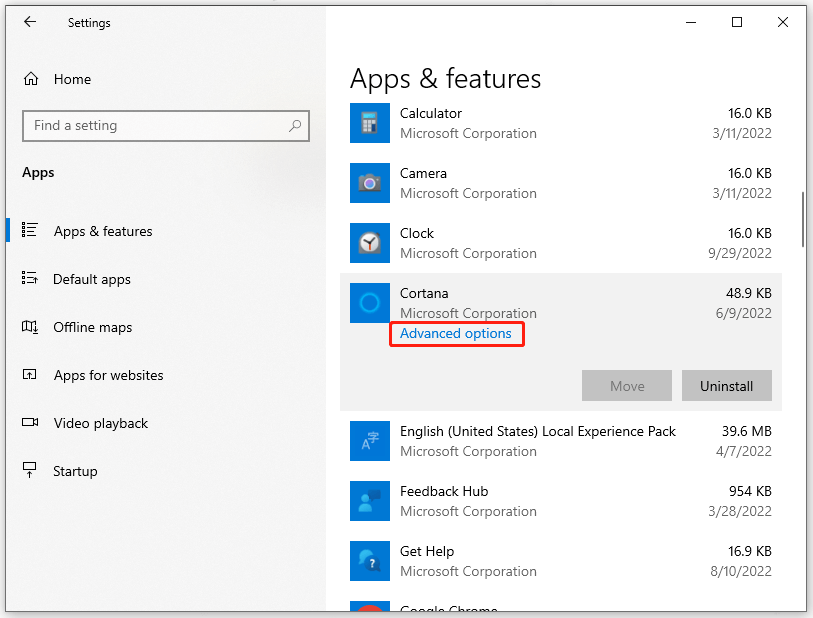
Step 3: Scroll down to choose Terminate to immediately terminate this app and its related process.
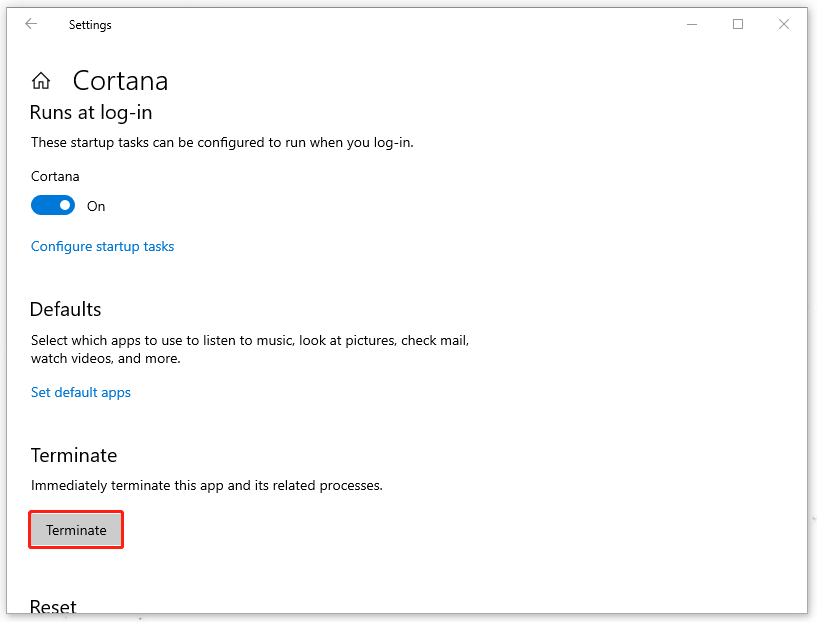
Then you can restart your computer and try indexing your files again.
Fix 4: Change Registry Value
If the search indexer was closed, you can reinitiate the entire Windows Search module by changing a registry value on your computer. That will help you restart indexing your files.
As for this method, you’d better make sure your registry has a backup plan. Anyway, changing the registry value can lead to severe results and the method is generally not used lightly.
Step 1: Open the Run dialogue box by pressing the Windows and R keys together and input regedit to enter.
Step 2: Then in the registry, follow the next location to find the target.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\FileChangeClientConfigs
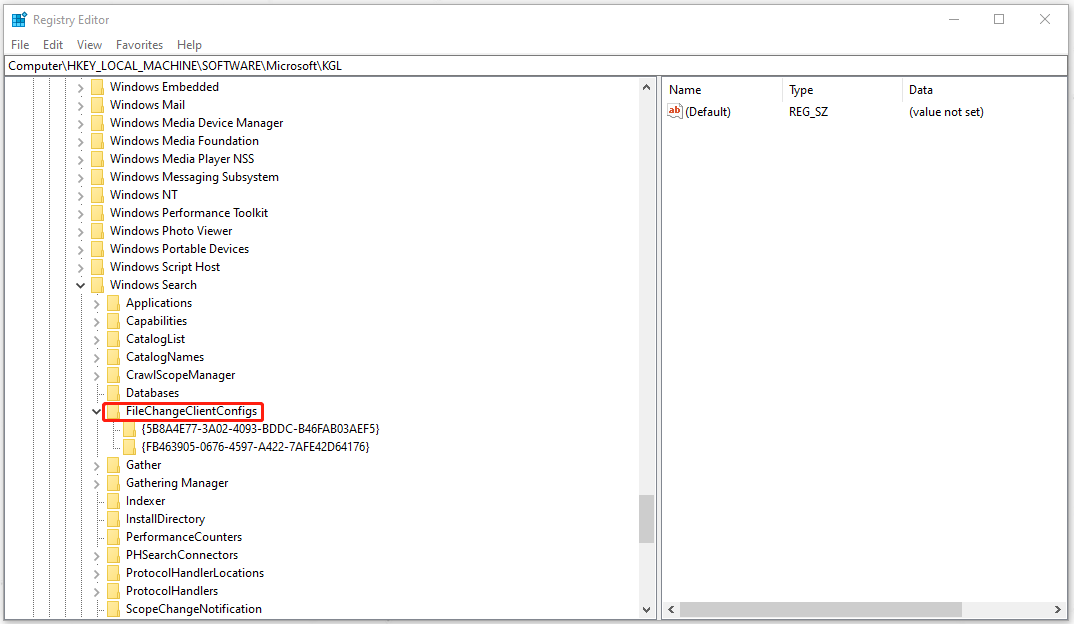
Step 3: You can rename the folder by adding something in the end. Just right-click on the folder and choose Rename from the list.
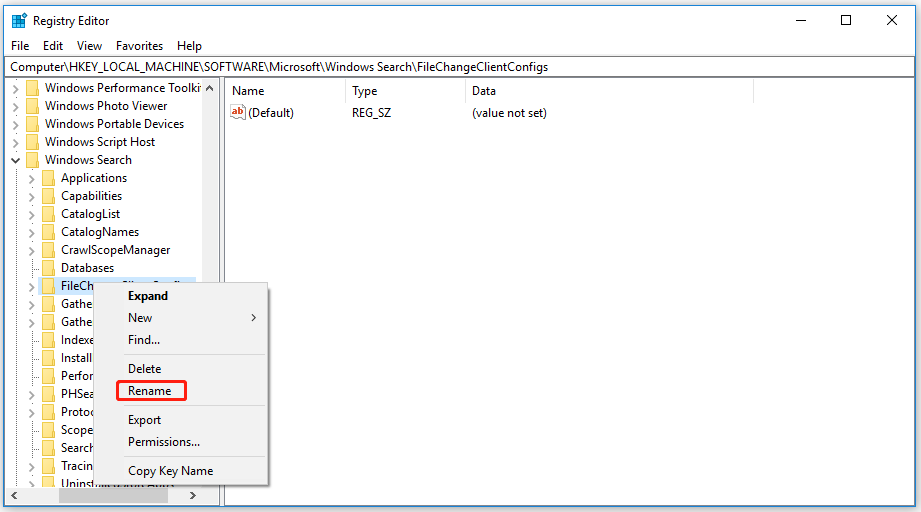
Then you can restart your computer and try fix 2 again to see if the issue persists.
Fix 5: Delete. BLF and. REGTRANS-MS files
If your indexing modules have been corrupted or the registry value has been missing, Windows 10 indexing is not running. You can delete some system files so that the computer will sense the difference and recreate the files, refresh the entire module, and start the indexing again.
Step 1: Open your File Explorer and navigate to the following file location:
C:\windows\system32\config\TxR
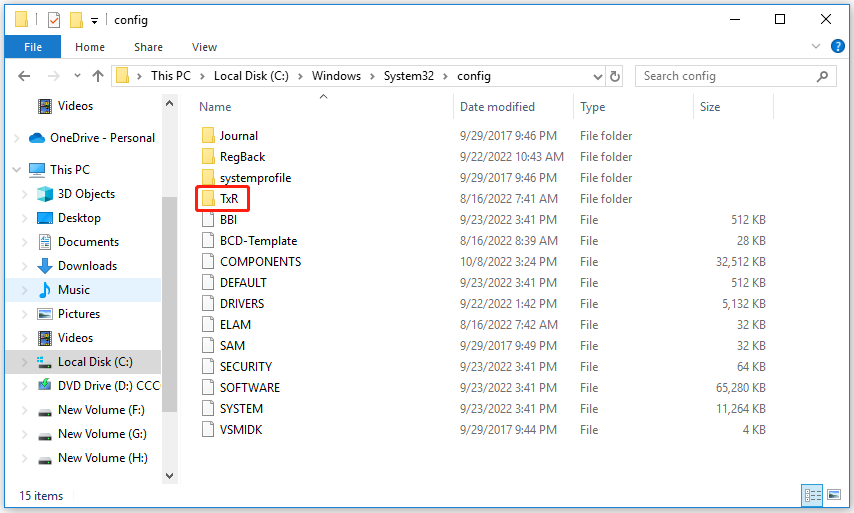
Step 2: Then go to the View tab and click on Options.
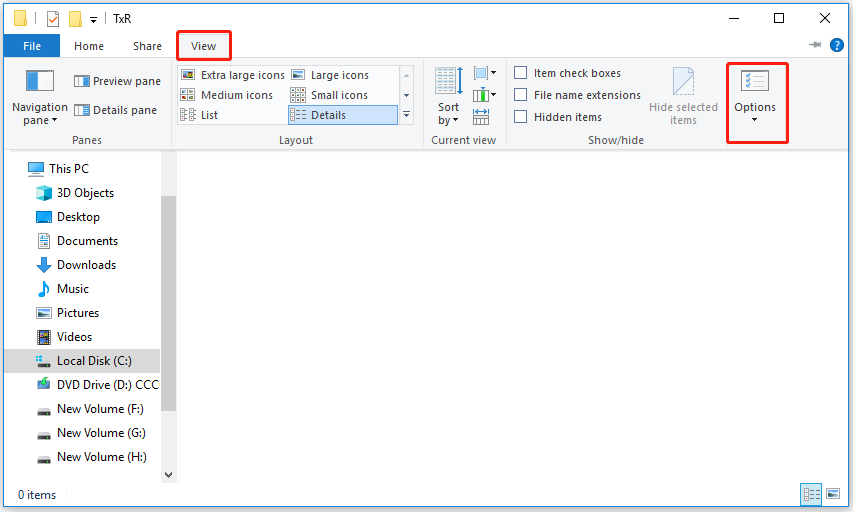
Step 3: In the pop-up window, switch to the View tab and scroll down to uncheck the option of Hide protected operating system files (Recommended). Then click Yes to confirm your choice when a warning appears.
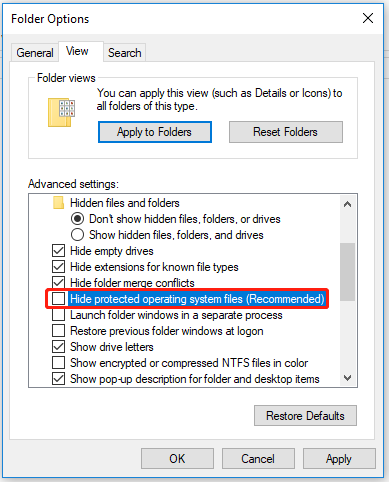
Step 4: Click on Apply to save your changes and then OK.
Step 5: Then in your TxR folder, delete all the files with the extension REGTRANS-MS and BLF.
Step 6: After that, restart your computer and check if the Windows 10 indexing is running or not.
Fix 6: Run the Search & Indexing Troubleshooter
Various troubleshooting techniques are present in Windows 10 and you can also find related troubleshooting for search and indexing.
Step 1: Go to Settings in Start and click on Update & Security.
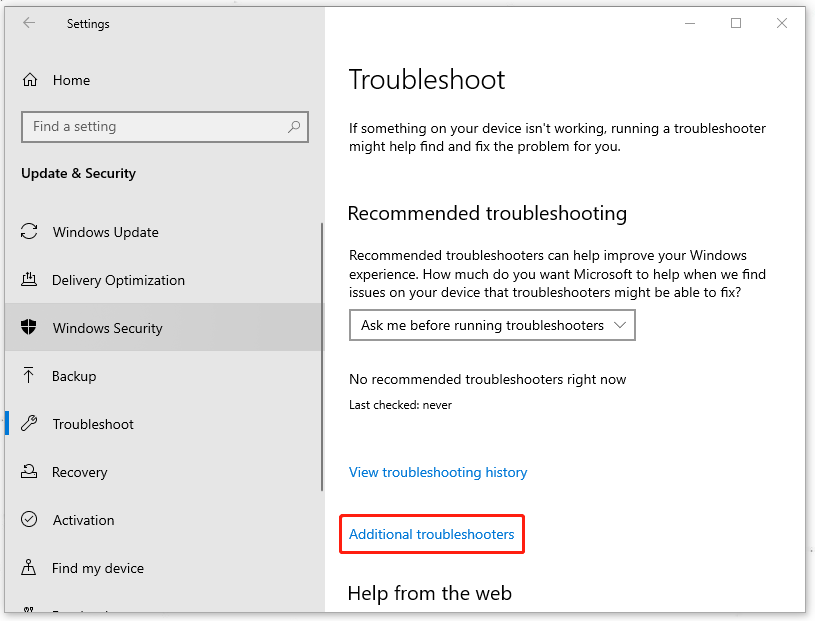
Step 2: In the Troubleshoot tab from the left menu, click on Additional troubleshooters.
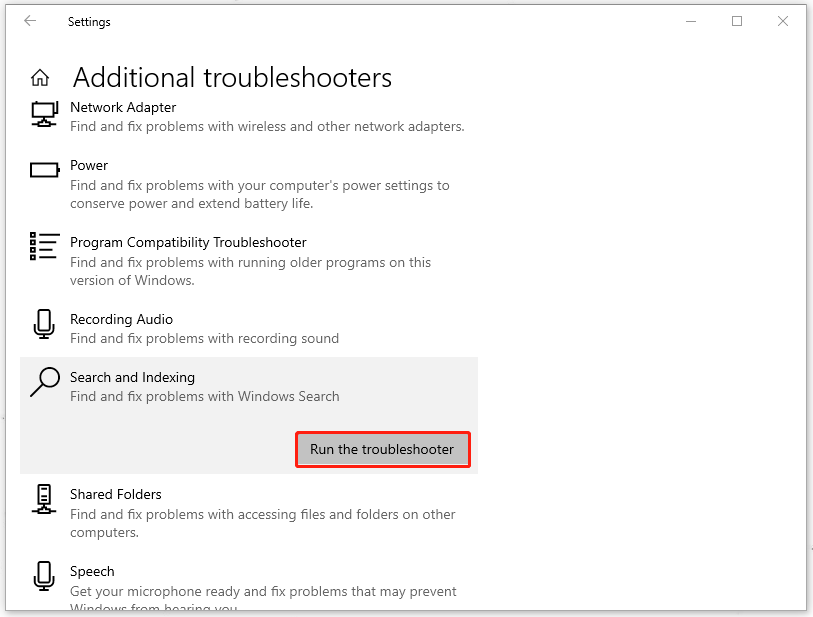
Step 3: Scroll down and choose Search and Indexing and then Run the troubleshooter.
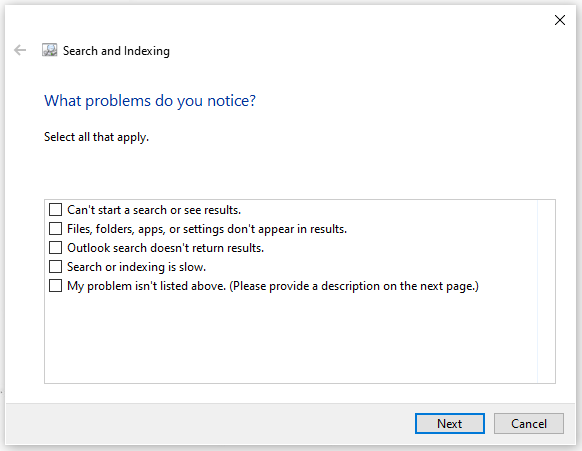
Then wait for a while, it will start the process and you will see a window asking you what problems you have. Just choose the options that are related to your issue and click OK. After the detecting process finishes, you can further describe your issue and follow the instructions on the screen.
Fix 7: Check LocalState Folder Permissions
You can fix the Windows indexing issue by enabling LocalState folder permissions. Do the following steps to make sure the folder permissions have been applied.
Step 1: Open File Explorer and show hidden files and folders by checking the option of Hidden items under the View tab.
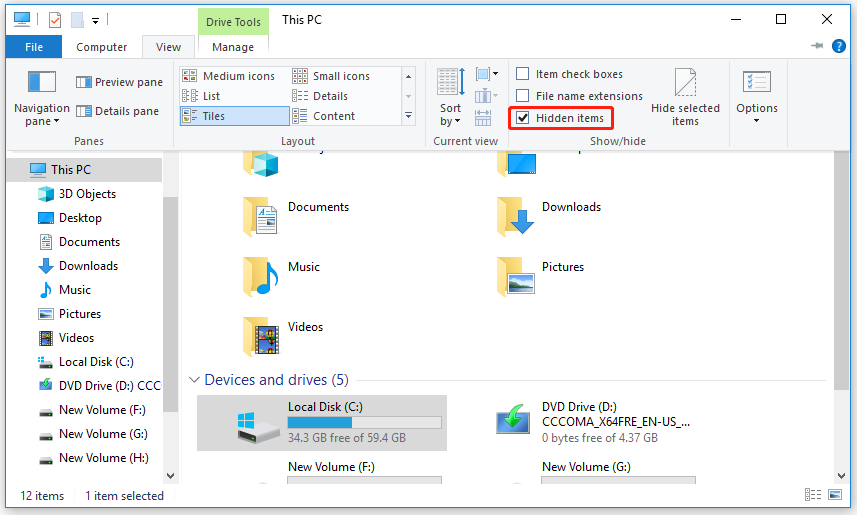
Step 2: Navigate to the following location:
C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Packages\windows.immersivecontrolpanel_cw5n1h2txyewy\LocalState
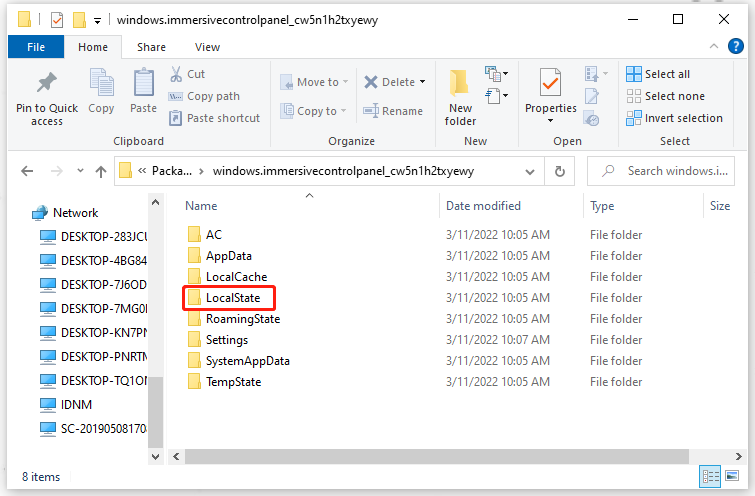
Step 3: Right-click on the LocalState folder and choose Properties.
Step 4: Click on Advanced… to check Allow files in this folder to have contents indexed in addition to file properties.
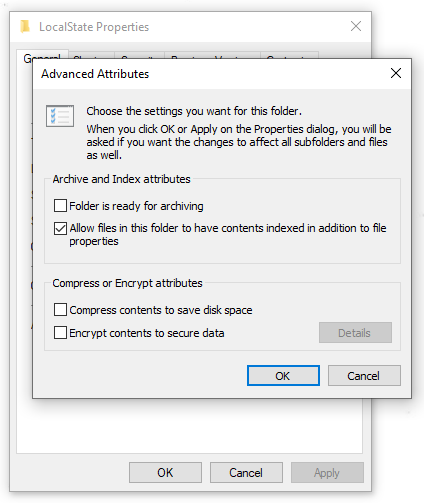
Then click OK to save it and try your indexing again.
Fix 8: Back up in Advance and Restore Your Computer
If all the above methods have been proven of no use, the worst situation may happen – you have corrupted system files beyond repair. In this way, the only fix is to restore your computer.
If you have created a system restore point before, you can use a system restore on Windows 10 that allows you to revert your laptop or desktop computer to an earlier point to resolve the issue without losing your files.
For more details about that, you can refer to this article: What Is System Restore Point and How to Create It? Look Here.
Apart from that, it is recommended to back up your data regularly in case any accident occurs. A committed backup expert – MiniTool ShadowMaker – can provide varied functions to backup, clone, and sync data. It can be your best trustworthy partner in the backup.
To enjoy the functions, you can download and install the program and you will get a free trial version for 30 days.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Open MiniTool ShadowMaker and click Keep trial to enter the program.
Step 2: Go to the Backup tab and click the Source section. Then you will see four options to be your backup contents – system, disk, partition, folder, and file, in which the system is set by default. You can directly click OK to save it.
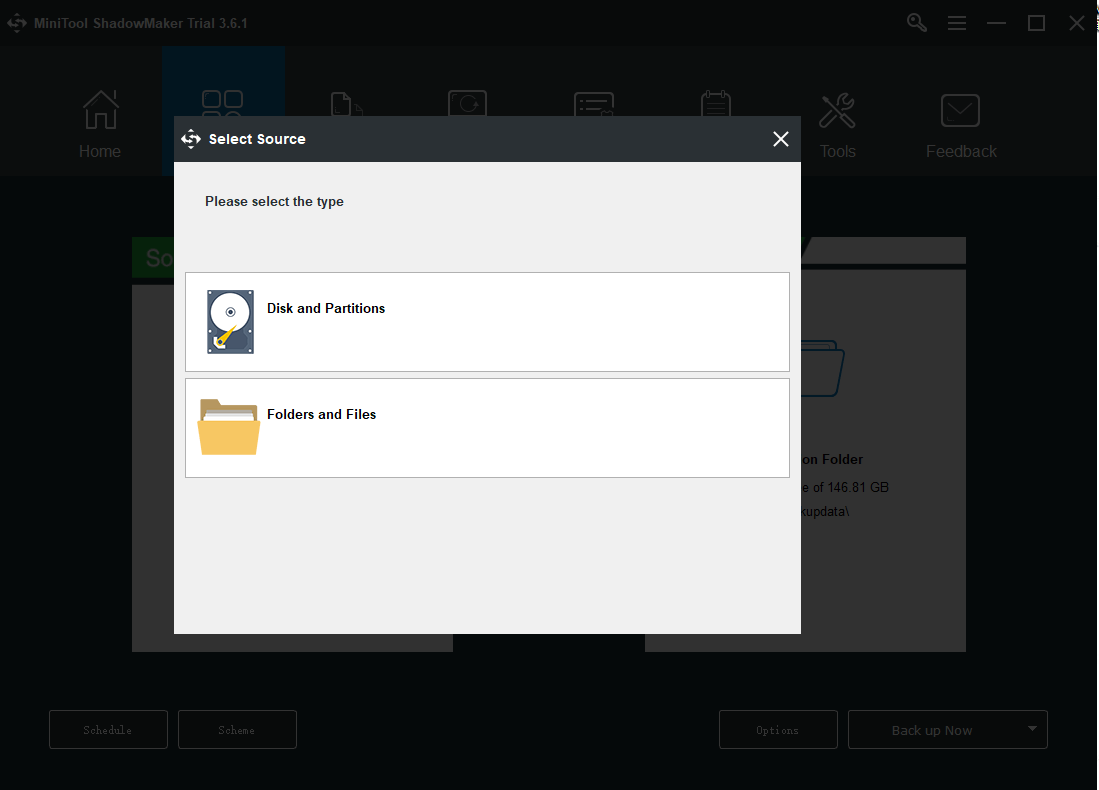
Step 3: Go to the Destination part and four options are available to choose from, including the Administrator account folder, Libraries, Computer, and Shared. Choose your destination path and click OK to save it.
Step 4: Click the Back up Now option to start the process immediately or the Back up Later option to delay the backup. The delayed backup task is on the Manage page.
Bottom Line:
The above contents have given you a step-by-step guide to resolving the issue that Windows 10 indexing is not working. Luckily, you can get rid of this issue by simply changing some settings or some errors are irrecoverable that requires you to restore your computer. Anyway, backup in advance can help bypass unnecessary troubles.
If you have encountered any issues when using MiniTool ShadowMaker, you can leave a message in the following comment zone and we will reply as soon as possible. If you need any help when using MiniTool software, you may contact us via [email protected].
Windows 10 Indexing Is Not Running FAQ
Indexing is paused by local battery-saving policy – according to some affected users, this issue is often created by a local group policy called 'Prevent indexing when running on battery power. If this policy is enabled, the indexing function will automatically be disabled while you're in battery-saving mode.
If you have a lower-powered computer with an older, slower hard drive, indexing can place a burden on the system resources, resulting in slower all-around performance as well. If you spend most of your time online working with data that is stored on the internet, the indexing burden should be pretty minimal.
Disabling indexing will increase the time it takes for Windows and other apps to return search results. So, if you have a fast CPU and a standard hard drive, you can keep indexing on. Since hard drives are slow to read, Windows will take longer to search for files without indexed data.
The index is where your discovered pages are stored. After a crawler finds a page, the search engine renders it just like a browser would. In the process of doing so, the search engine analyzes that page's contents. All of that information is stored in its index.


User Comments :