Several days ago, I browsed forums for Windows partitioning related problems as usual and surprisingly found a huge number of users asked the same question – does partitioning a hard drive affect computer performance. Disappointingly, most of them haven’t got a satisfying answer, so we wrote this post and hope it contains necessary information those folks want to know.
This post mainly consists of 3 parts: what is partitioning, does partitioning affect performance, and how to partition a hard drive properly.
Now, let’s begin.
Overview of Partition Hard Disk in Windows
When asking what disk partitioning is, most of you would answer it is to separate one physical hard disk into one or more independent partitions. Indeed, when searching such a question on the internet, users are always given this answer, and Wikipedia also says:
“Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on a hard disk or other secondary storage, so that an operating system can manage information in each region separately”.Wikipedia
But as a matter of fact, to divide a physical hard disk into multiple parts is just one of the partitioning operations, which might be a brand new point of view for most people. For a brand new or never-used hard disk you have to initialize it to either MBR or GPT at first, which determines partition style, otherwise creating partition is not allowed.
After partitions have been created, there are still lots of other partitioning operations to do, such as defrag/format/delete/resize/merge/split/align partition, change partition cluster size, convert file system between NTFS and FAT32, convert partition style between MBR and GPT, etc.
Reading here some of you would be more eager to know whether partitioning affects computer performance or not. If influence, how? For specific answers, please keep reading this post.
Does Disk Partitioning Affect Performance?
You may be curious about these two questions: does partitioning a hard drive increase performance or does partitioning slow down the computer?
Actually, you can’t simply say Yes or No to answer these questions, because just a part of partitioning operations (not all) influence computer performance, among which some increase performance, some make no sense to performance, and the remaining slow down the computer. Then, let’s see the details from the following part.
What Partitioning Operations Affect Computer Performance
Among all partitioning operations mentioned above, to create partitions, defrag partition, enlarge partition, adjust partition cluster size, and align partition could impact the computer performance. The remaining ones have little or no influence.
1. Create Multiple Partitions on One Physical Disk
Creating multiple partitions on one physical hard disk can either increase performance or decrease performance. Whether to create multiple partitions or not, it depends on your own situation.
To increase:
Having multiple partitions makes it possible to save data by category, for example, one partition for the operating system, one for frequently used data, and one for games, which is faster and more convenient for us to access, organize and manage data.
It can also raise overall computer performance on systems where smaller file systems are more efficient. For instance, large hard disks with multiple NTFS file systems typically are always having small sequentially accessed Master File Table (MFT for short), and it generally takes less time to read this kind of MFT than the bigger MFT of smaller partitions.
It reduces the time for diagnostic tools such as CHKDSK and Disk Defragmenter to run. After all, scanning a huge partition will cost so much time.
To decrease:
It reduces overall disk performance on systems where data is accessed regularly and in parallel on multiple partitions, because it forces the disk’s read/write head to move back and forth on the disk to access data on each partition.
Compared to a single partition of the same overall size, having multiple partitions increases disk fragments, because it lowers the average size of contiguous free blocks on each partition after the same amount of data has been written to them.
2. Defrag Partition
Microsoft says Disk Defragmenter analyzes local volumes and consolidates fragmented files and folders so that each occupies a single, contiguous space on the volume. As a result, our system can access files and folders and save new ones more efficiently.
Therefore, if your computer employs traditional hard disks which read and write data via a magnetic head, to defrag partition will raise computer performance. But if you are using SSDs that do not need to spin or seek to locate data, defragment is not suggested, because it may reduce the lifetime of your SSD.
To be specific, the storage sectors on an SSD have a limited number of writes, which is often fewer on cheaper drives, and defragmenting will cause many more writes as your defragmenter moves files around. Thus, the lifespan of SSD would be reduced.
You might be interested in this post too, 6 Things You Shouldn’t Do With Solid-State Drives.
3. Extend Partition
Here, we mainly refer to enlarging boot partition. On HDD, when this partition is running in low disk space, Windows will cost much time to locate needed files and programs, and at the same time there will be no enough space for swap files and temporary files. So does an SSD. When an SSD has little free space, it has a lot of partially filled blocks. When we are writing a file, it will have to read the partially filled block into its cache, modify the partially-filled block with the new data, and then write it back to the hard drive, thus costing more time.
Therefore, when boot partition (it is always C drive) is running in low disk space, you’d better enlarge it to maintain performance.
4. Change Partition Cluster Size
A cluster is the smallest logical amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file, and one cluster can only hold content of one file. If a file is 3 times larger than cluster size of the partition, it will occupy 3 clusters.
When we are going to view the file, hard disk read/write head will move to 3 different clusters, thus increasing access time. On the contrary, if file size is equal to or even smaller than cluster size, the file will only take up 1 cluster, thus read/write head just moves to one cluster. So does writing files.
Therefore, partitions saving large files had better be set with large cluster size to quicken read/write speed.
5. Align Partition
If a partition is misaligned, its physical sectors and actual clusters will be shifted due to the use of 512e sector, thus reading data saved in one cluster will access 2 physical sectors, and writing a file will use 2 physical sectors at least. As a result, computer performance is largely decreased. For more details of partition alignment, please see 4K Alignment.
Under this situation, as long as we make physical sectors and clusters aligned via aligning partition, all issues could be solved.
Conclusion: these 5 partitioning operations could affect our computer performance. As long we do it properly, computer performance might be increased to a large extent.
How to Partition a Hard Drive Reasonably to Optimize Computer Performance
Now you have known the answer to this question “does partitioning affect performance”. Next, it is your turn to reasonably partition a hard drive to improve the performance of the computer.
To partition hard disk in Windows, the built-in tool – Disk Management tool can help you complete basic partitioning operations, like create partition and resize partition. However, it has limits in resizing partitions (both extend and shrink) and cannot complete advanced operations like change cluster size and align partitions.
Therefore, the best free partition software, MiniTool Partition Wizard is necessary since it can easily complete these operations mentioned. Just download its Free Edition to have a try.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Create More Partitions If Your OS, Personal Files, Games, etc. Are Saved in One Partition
To create a partition requires unallocated space or free space on the hard disk. If there is no such space, please shrink the existing one to release.
Step 1: To shrink a partition, choose the target partition and click Move/Resize Partition. Just move the handle towards the left side or right side to free up some disk space.
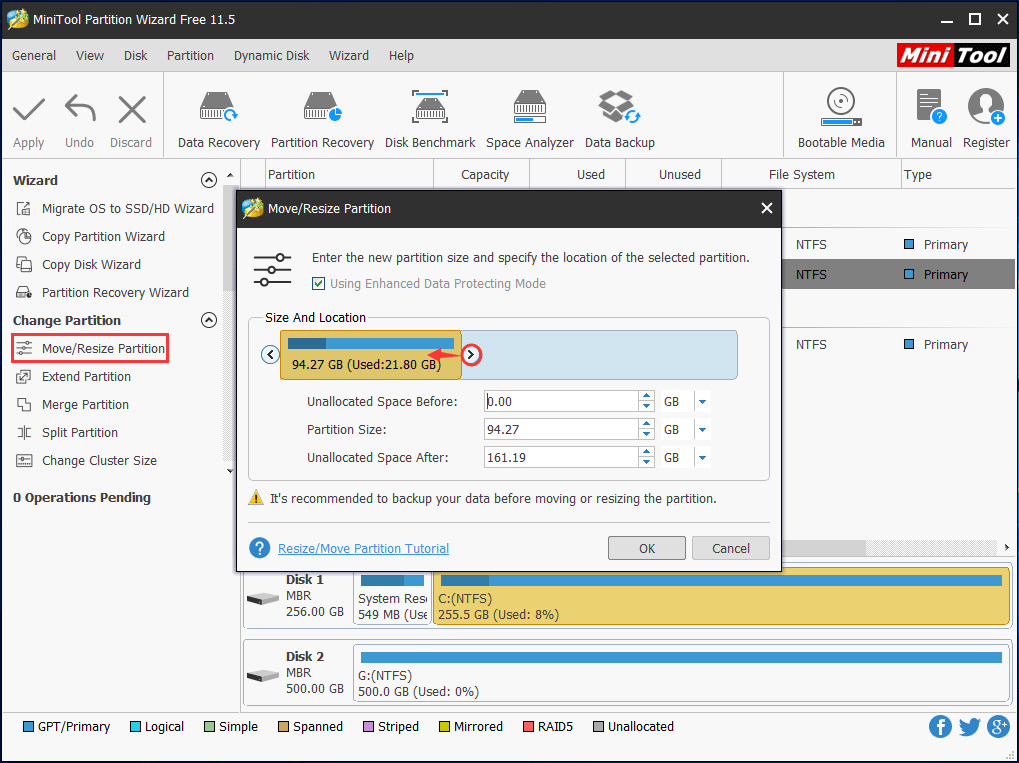
Step 2: Once an unallocated space is made, click it and select Create Partition.
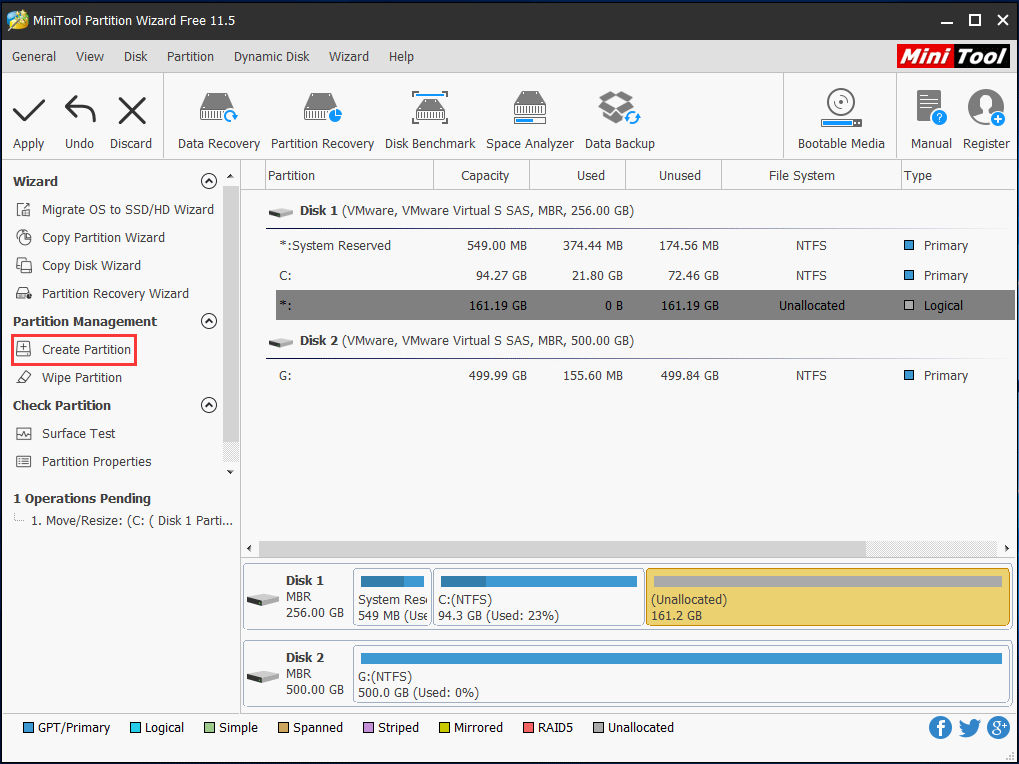
Step 3: Set properties like partition size, drive letter, file system, and cluster size for this new partition.
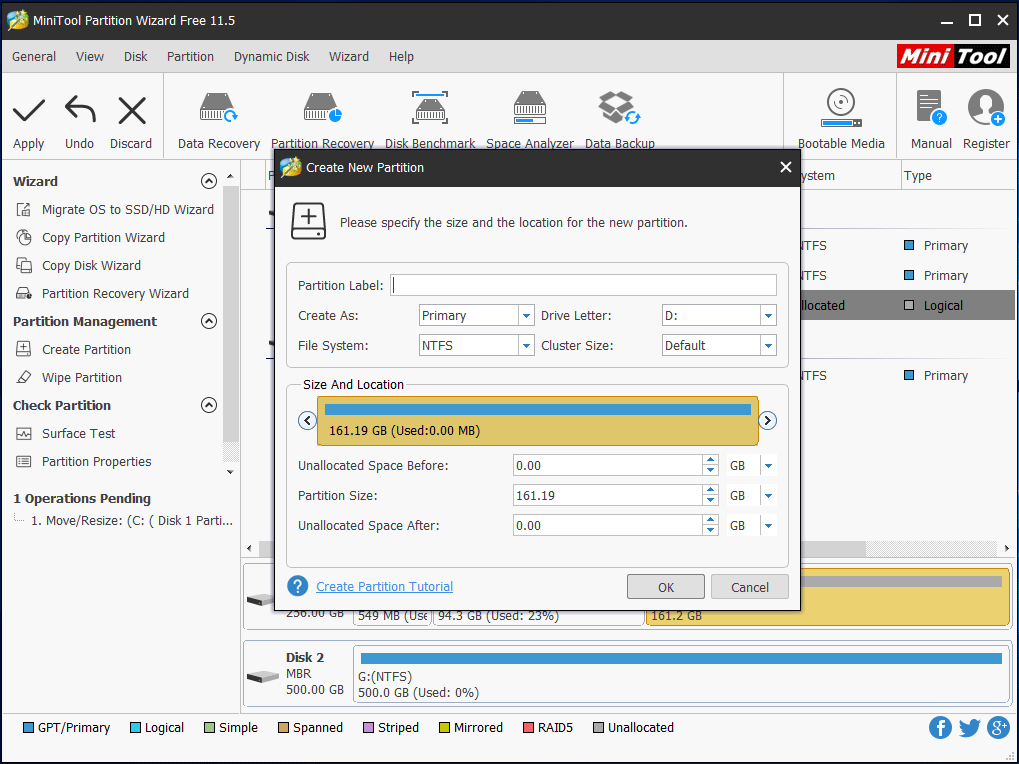
Step 4: Finally, hit the Apply button to execute all changes. With simple steps, you can partition hard disk in Windows easily.
2. Extend System Partition with Low Disk Space
Here we recommend you to use the Bootable Edition of MiniTool Partition Wizard (included in a paid edition) to increase partition size in WinPE to avoid system accident after partitioning.
Related articles:
- How to Build Bootable CD/DVD/USB Flash Drive with Bootable Media Builder?
- How to Boot from Burned MiniTool Bootable CD/DVD Discs or USB Flash Drive?
Step 1: In the MiniTool WinPE, note that the drive letter varies. Choose the system partition and click Extend Partition.
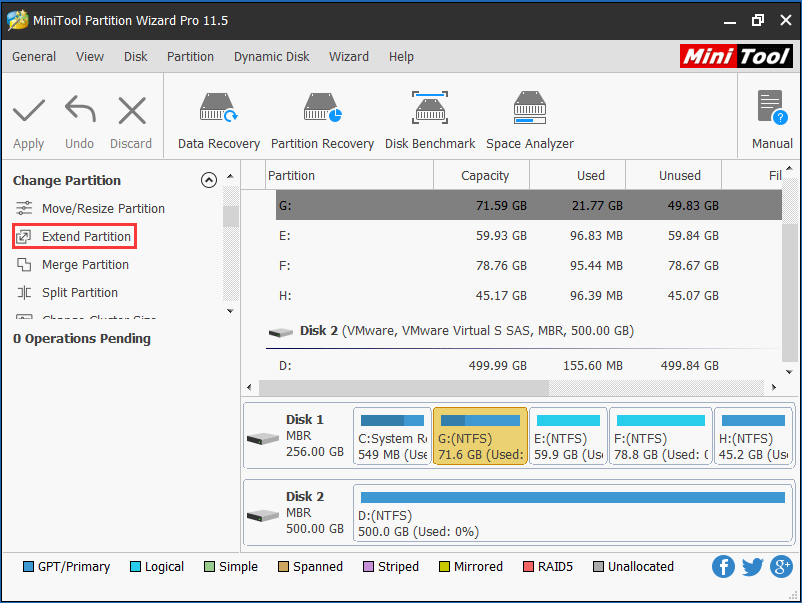
Step 2: Take some free space from another big partition or an unallocated space and click OK button.
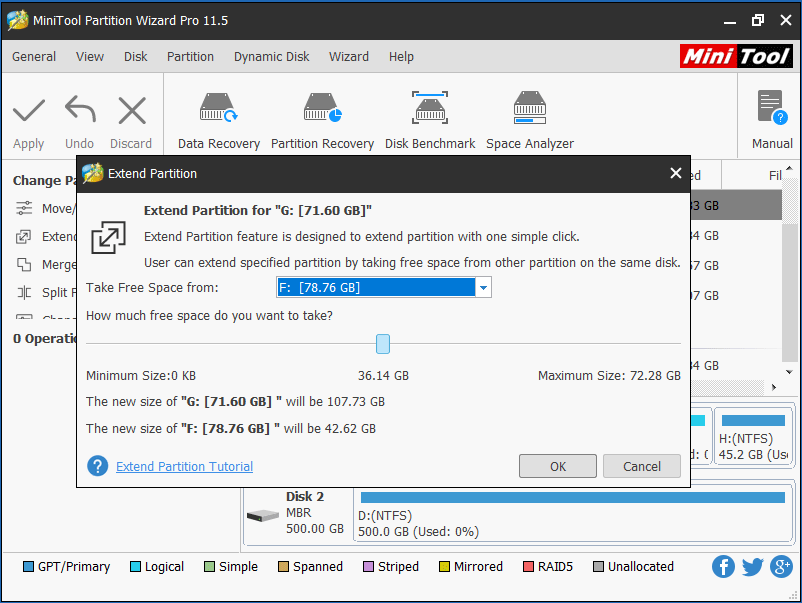
Step 3: At last, execute the change by hitting the Apply button.
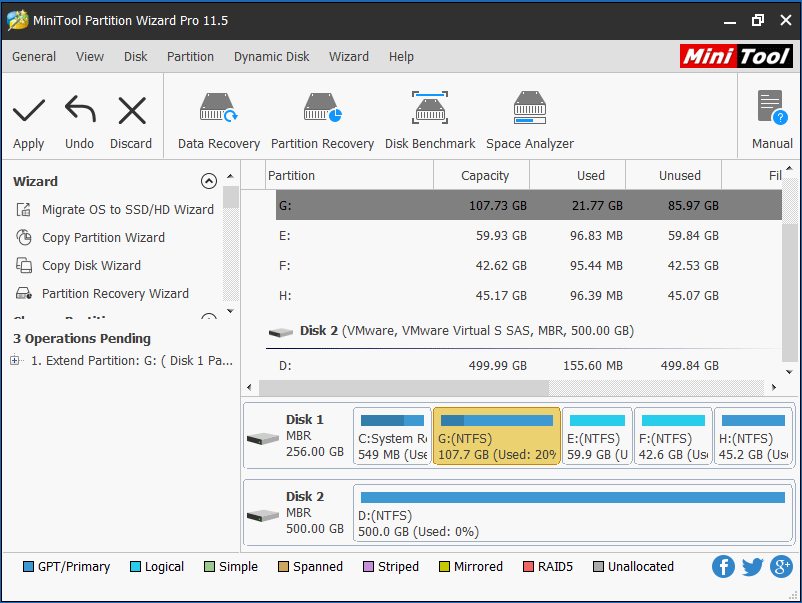
After extending system partition, your computer may run fast. From here, you know the answer to the question “does partitioning affect performance” is Yes.
3. Defrag Partition Regularly If You Write and Read Data to This Partition Frequently
To defrag a partition, you’ll need to run Windows snap-in Disk Defragment tool.
Take Windows 10 as an example.
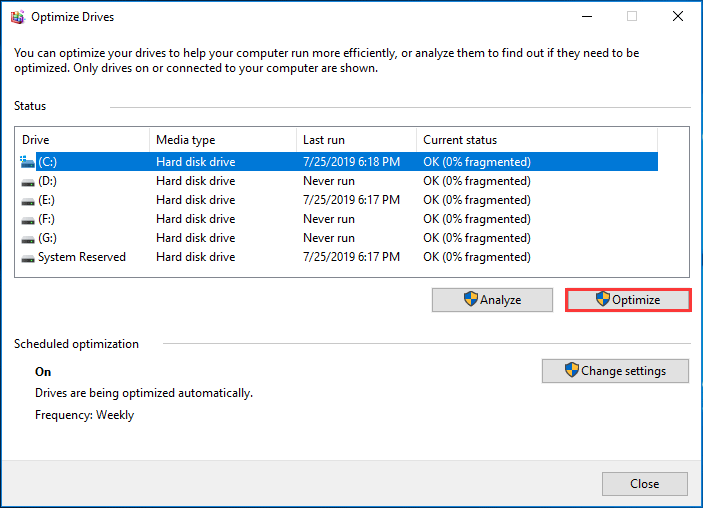
Just type defragment in the search box and choose Defragment and Optimize Drives from the search results. Then, select the partition that you want to defrag, and choose the Optimize button in Windows 10. After that, this tool will do its job automatically.
For more details, please see Disk Defragmentation.
4. Enlarge Cluster Size If the Partition Saves Large Files
Cluster size is also called allocation unit size in Windows. To change it, you can make use of the format command, but formatting will undoubtedly cause data loss. For lossless conversion, you can try using MiniTool Partition Wizard since it offers you a feature called Change Cluster Size.
MiniTool Partition Wizard Free is not allowed to change cluster size, so you need to purchase Professional or more advanced editions. Purchase here with enjoying discounts. However, before buying, you can download the demo version to have a try.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Firstly, please start the program to get its main interface. Then, select the partition whose cluster size is unreasonable and choose Change Cluster Size function from the left side.
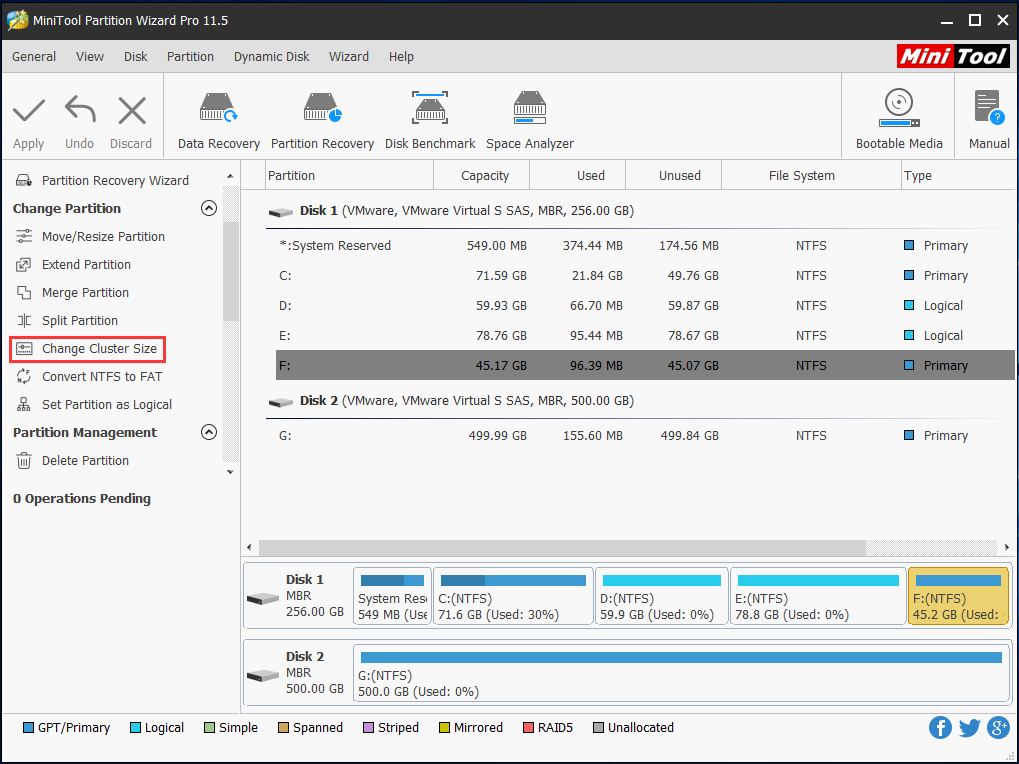
Step 2: Next, choose a reasonable cluster size from the drop-down menu and click Yes.
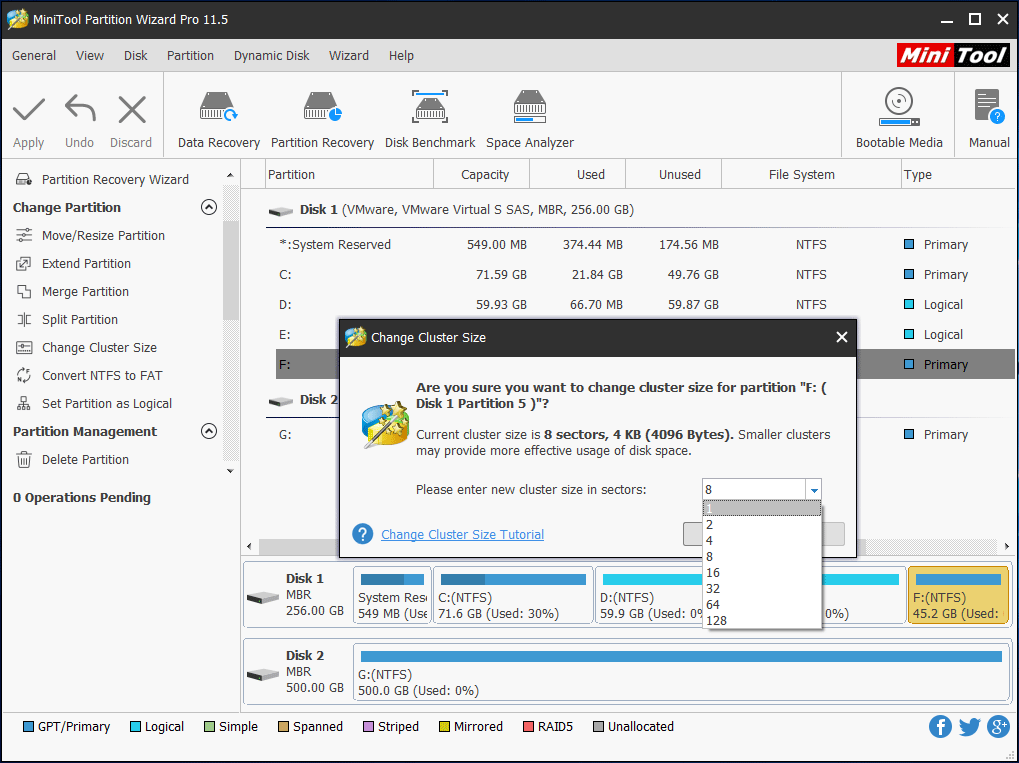
Step 3: At last, click on the Apply button to make this change performed.
5. Align Partition(s) If You Are Using SSD
Though partitions created under recent Windows OS will be aligned automatically, previously aligned partitions might become misaligned due to later partitioning operations like resize and copy. Therefore, it is also very necessary to align partitions of SSD.
Nevertheless, Windows doesn’t provide users with features to do such an operation, so you have to use a third-party program. MiniTool Partition Wizard is a freeware for Windows non-server users.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Start the program and you can see the main window below. To align a partition, please select it and choose Align Partition from the left side.
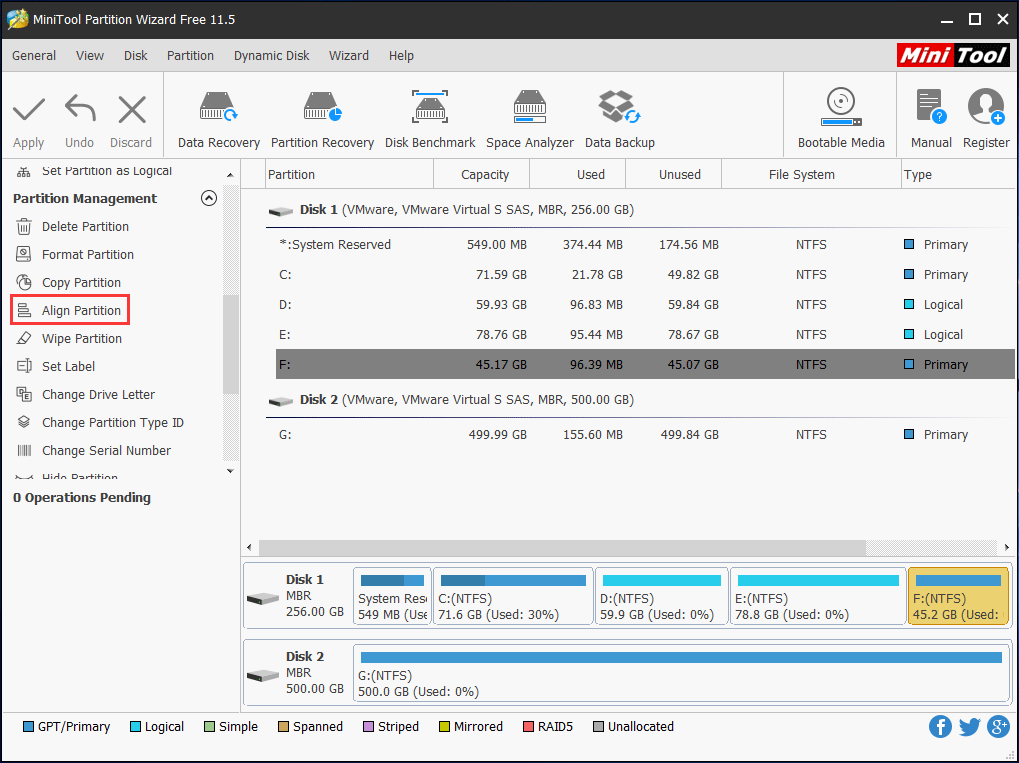
If the partition is already aligned, this partition manager will say “The specified partition does not need to change partitions alignment. It is already aligned“.
If MiniTool Partition Wizard finds it misaligned, you’ll see a pending operation on Operations Pending area. At this time, just click the Apply button to make this pending operation finally performed.
After doing these partitioning operations, you can make a benchmark test to see whether your computer performance is increased or not. Just find a free testing program from the internet.
Bottom Line
Does partitioning affect performance? You must know the answer after reading this post, as well as how to partition a hard drive reasonably in Windows. To optimize computer performance, just follow the instructions mentioned above.
Should you have any other problem with disk partitioning, leave us a message in the comment area or contact [email protected] and we will answer it soon.
Should I Partition My Hard Drive FAQ
- Install multiple operating systems
- Separate valuable files to minimize corruption risk
- Allocate specific system space, data, and applications for specific uses
- Easy to reinstall Windows on a separate partition
- Use many file systems
User Comments :