An Overview of VirtualBox
VirtualBox, a cross-platform virtualization application, allows users to install operating system like Windows, MacOS, Solaris and Linux without changing your current computer system. By using VirtualBox, you can create and run a guest operating system (virtual machine) via a window of the host operating system.
As virtual machine (VM) has a self-contained environment, you can carry out some operations without the risk of damaging the host operating system. Based on that, VirtualBox has some other advantages. They are summarized as follows.
- Easy to install and use
- Free
- Run other systems safely
- Can test your own development projects in multiple system environment
- Can run on places ranging from embedded system to laptop
- Suitable for testing and disaster recovery
In a word, VirtualBox grants you lots of benefits.
Recommendation: Quick Fix VirtualBox Result Code: E_Invalidarg (0x80070057)
Why to Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
You are required to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox on many cases. For instance, when you are going to try out some software without damaging your present operating system, migrate from Windows or MacOS to Linux, or test applications/network, you need to do that.
In addition, installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox as a virtual machine offers you some benefits. For instance, you are able to create a snapshot and roll back changes to the previous VM state if there’s something wrong with environment.
It is easy to clone a VM, copy a VM on different VirtualBox supported by host operating systems. To sum up, it is useful to install VirtualBox Ubuntu.
Requirements to Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
In order to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox successfully, you have to fulfill the requirements below. Otherwise, you may fail to install Ubuntu VirtualBox or encounter some errors.
# 1: Enough Memory and Disk Space
Installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox requires sufficient disk space and memory. This operation needs at least 4GB RAM and 30GB free disk space. Hence, you should firstly perform a PC full specs check to see the detailed information of RAM and available disk space.
If you find that RAM doesn’t fulfill the requirement, you can add some RAM via the help of this guide. If the available free disk space is not enough, you need to take some actions to increase disk space. Well, you are able to enlarge disk via a professional partition managing program.
MiniTool Partition Wizard probably is what you are seeking for. It is a partition manage expert, which allows you to perform various operations associated with partition such as Surface Test, Disk Benchmark, Check File System, Extend Partition, Format Partition, as well as Wipe Disk, etc.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
The Extend Partition is recommended in the following two cases. And you can refer to the steps below to increase disk space.
1. Extend a partition to non-contiguous unallocated or free space.
2. There is no unallocated or free space on the disk drive.
Step 1: Open MiniTool Partition Wizard to get its main interface, and then click on the partition to enlarge and click the Extend Partition option in the left pane.
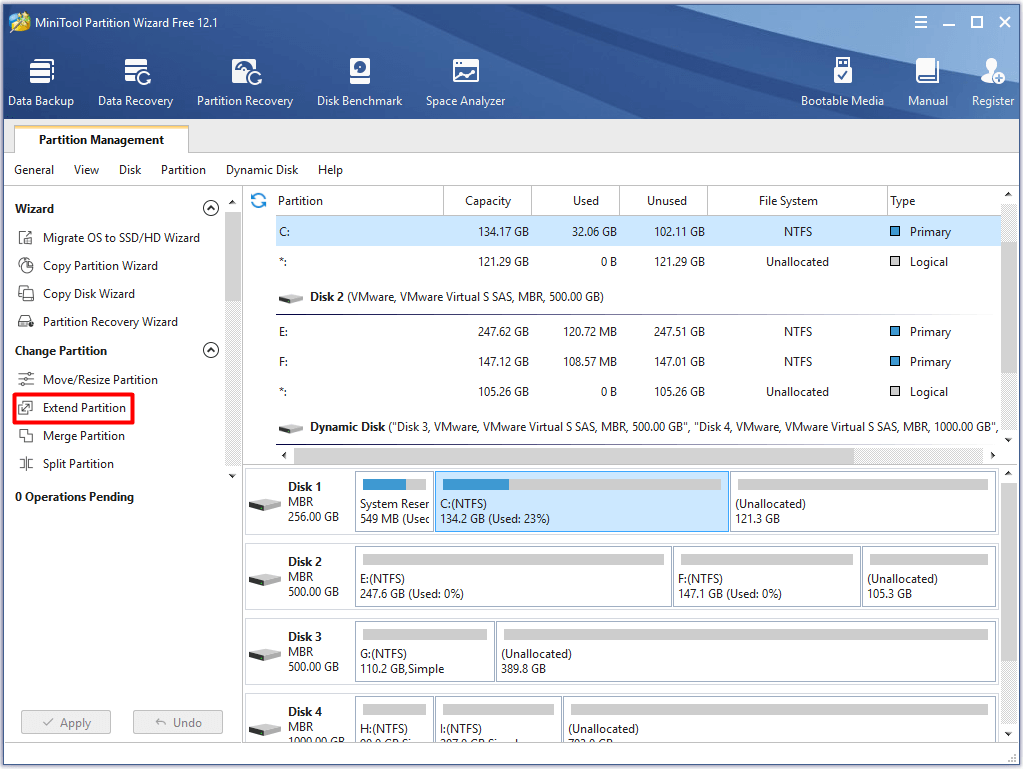
Step 2: In the next window, choose a drive that you want to take free space from and move the handle to decide the space to extend. Then click OK and Apply to save and execute the changes.
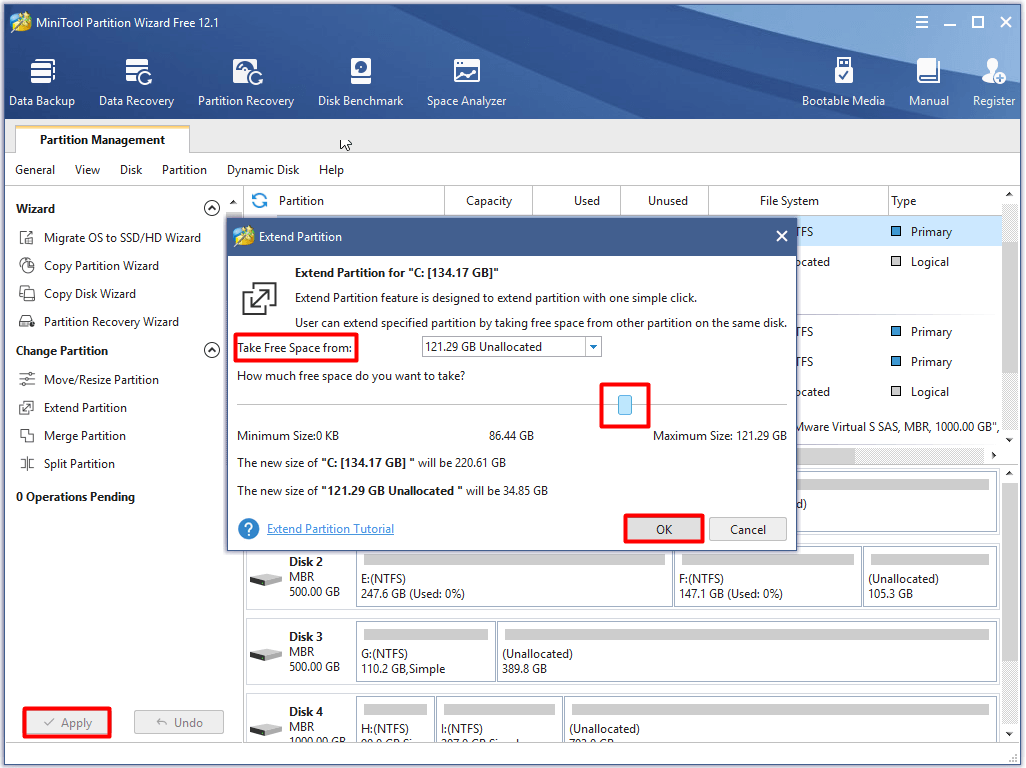
To move/resize a partition, make sure that there is available contiguous unallocated space on the disk. Then, refer to this tutorial.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
As the picture shows, choose the partition to move/resize and click on Move/Resize option in the left action panel. Adjust the size and location of the target partition by moving the handle in the prompted window. After that, click OK and Apply to save and carry out the changes you’ve made.
# 2: Good Internet Connection
A good Internet connection is also vital for installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox. You need a good Internet to download the software and Linux ISO.
# 3: Intel VT-x or AMD-v Hardware Virtualization Feature Is Supported and Enabled
Besides, the CPU (Central Processor Unit) of your computer must support Intel VT-x or AMD-v hardware virtualization feature. More importantly, you should ensure that the featured is enabled in UEFI/BIOS before installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox.
How to Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
This section will show you how to install Ubuntu on Windows 10 using VirtualBox. As the whole process is complicated, we divide the whole process into 5 parts. Now, check them one by one.
You may also like this: How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide 2023]
Part 1: Download Ubuntu
You can start the Ubuntu VirtualBox installation operation by downloading and installing Ubuntu. Here are steps for that.
Step 1: Move to the official website of Ubuntu and click Download button to start downloading.

Step 2: Then store the ISO file as you are prompted.
Part 2: Download and Install VirtualBox on Computer
As VirtualBox is not a built-in program on the computer, you need to download and install it manually.
Step 1: Go to the official website of Oracle VirtualBox to download it.
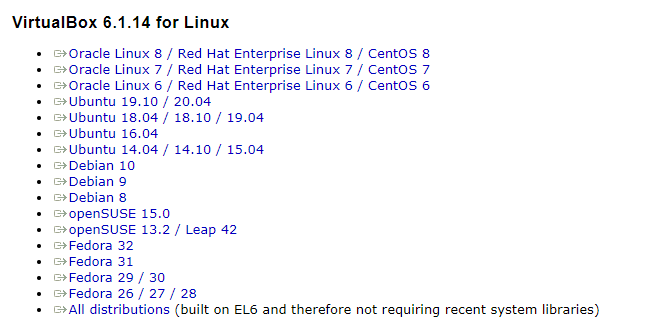
1.Click here to move to the website. After entering this page, click Download VirtualBox button.
2.In the next page, click on Linux distributions.

3.From the listed packages, download a suitable one.
Step 2: Click on the file you just downloaded and then you will get the following window. Click Next to go on.
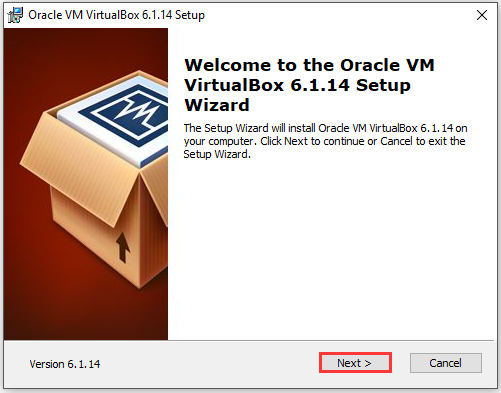
Step 3: In the prompted window, click the Next button.
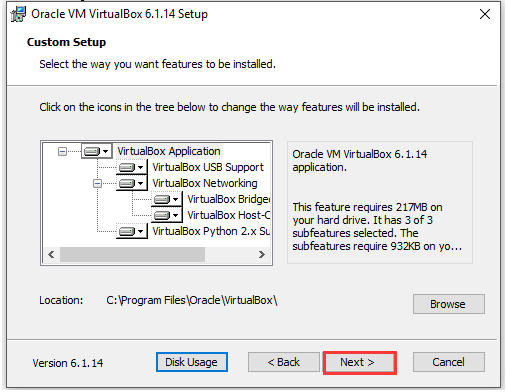
Step 4: In the next window, click Yes.
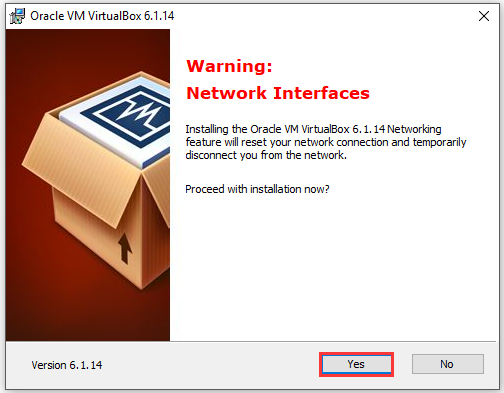
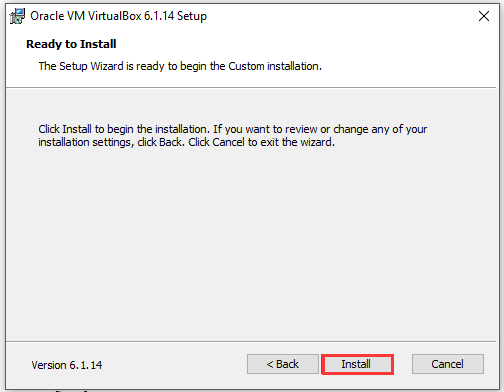
Step 5: Once you click the Install button, the program will be installed automatically.
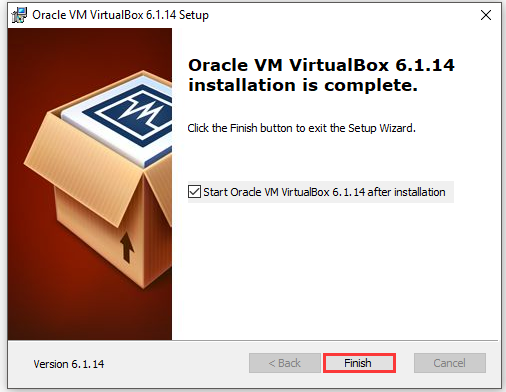
Step 6: After finishing the installation, click Finish.
Part 3: Set up a Virtual Machine
When the VirtualBox download and installation processes end, you should set up a virtual machine via VirtualBox. After completing the steps above, you will be prompted with the following window. Follow these steps to set up a virtual machine now.
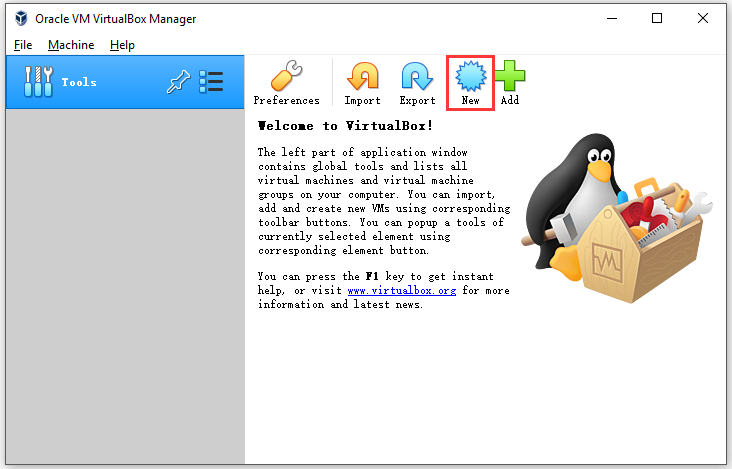
Step 1: Click on New tab in the Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager window.
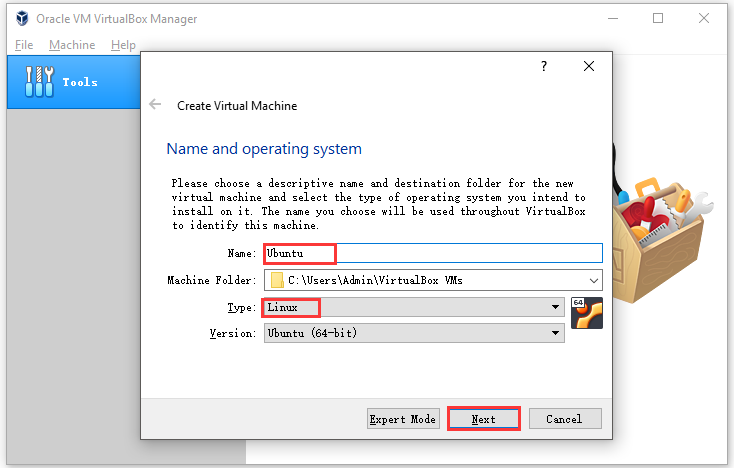
Step 2: In the elevated window, type Ubuntu in the Name section. Choose Linux as the Type and Ubuntu (64-bit) as the Version. Then, click Next.
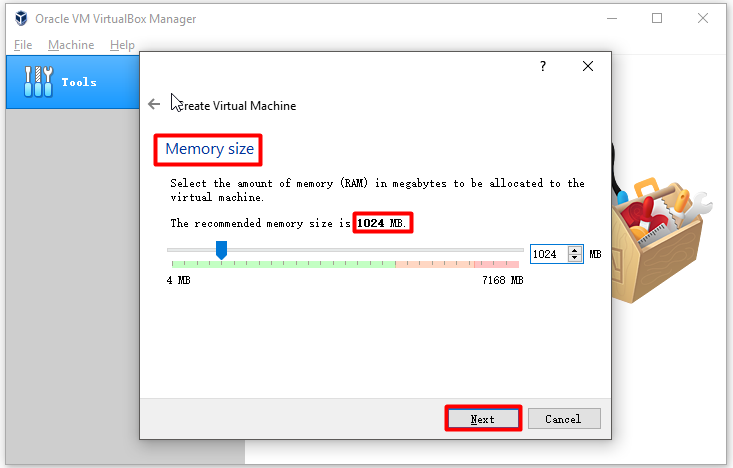
Step 3: At this window, set the memory size. Generally speaking, the memory size will be set at an ideal value. If not, you need to set it by yourself. You can refer to the recommended size. Then, click Next.
Step 4: In the Create Virtual Machine window, click the Create button.
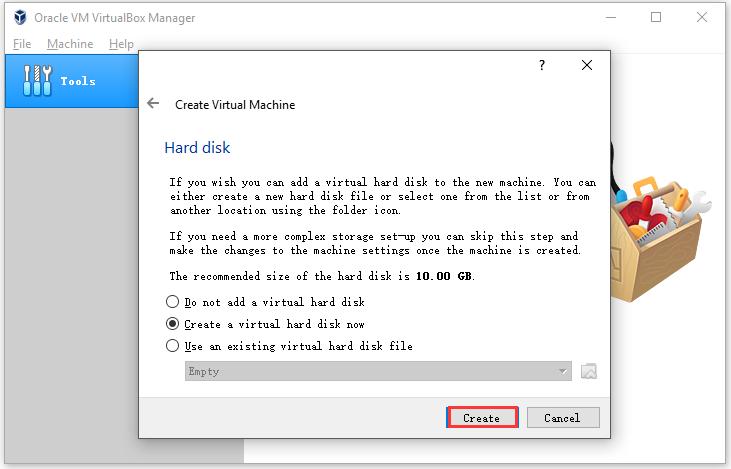
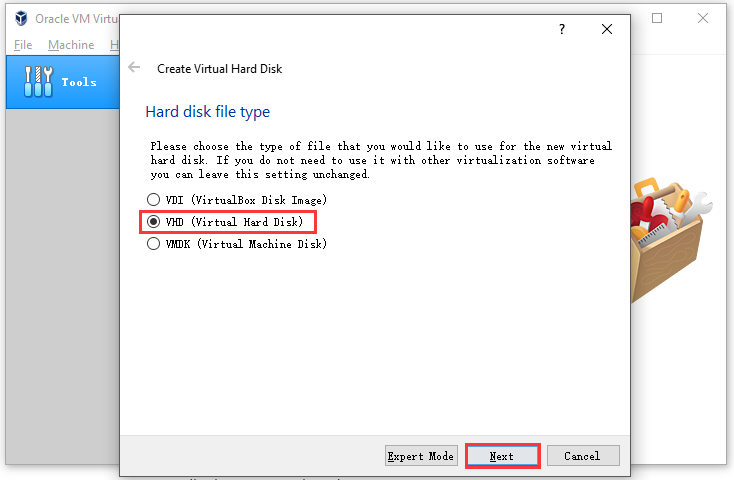
Step 5: You need to choose a hard disk file type in this window. Choose VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) and click on the Next button. This hard disk serves as the hard disk of the virtual Linux system that stores files in this system.
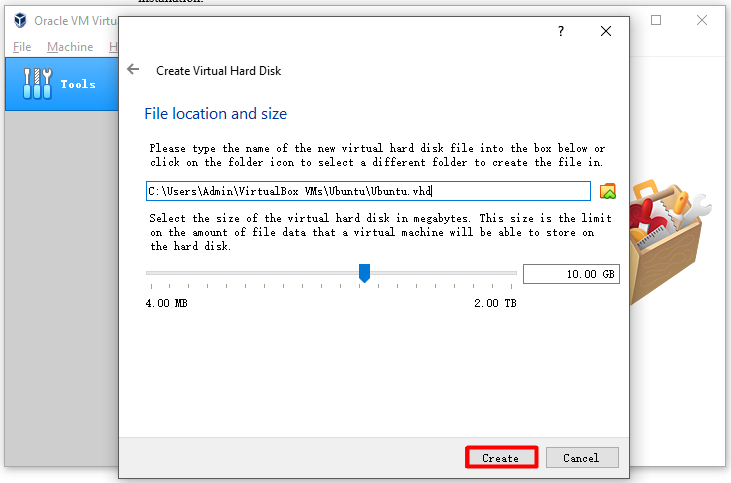
Step 6: If you are prompted with the window for choosing storage on physical hard disk, click Next directly. Either to choose Dynamically allocated or Fixed size is ok. In the File location and size window, you can configure the size or follow the default size. Then click Create to start creating.
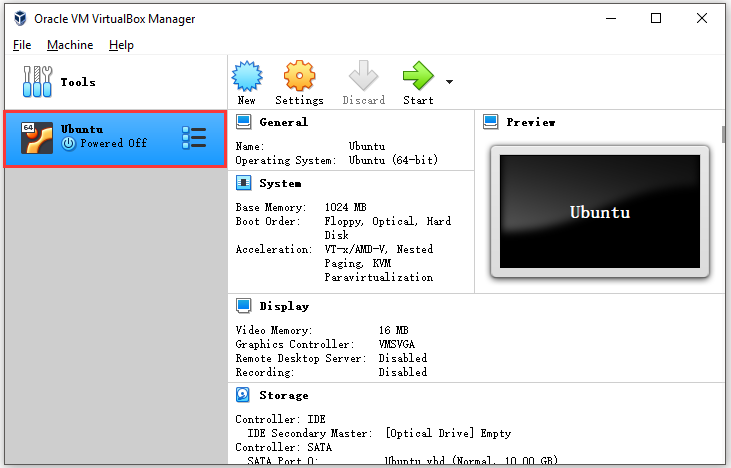
Part 4: Enable the Ubuntu
Now, you can enable the Ubuntu on VirtualBox with the following steps.
Step 1: Double click the Ubuntu option in the left pane. Then a menu will open by itself.
Step 2: In the prompted window, click the icon at the right bottom of the window. Select the ISO file that you stored on the computer and click the Open button.
Step 3: Then click the Start button to continue.
Step 4: In the next prompted window, click Install Ubuntu.
Step 5: After choosing the two listed options, click Continue in the Preparing to install Ubuntu window.
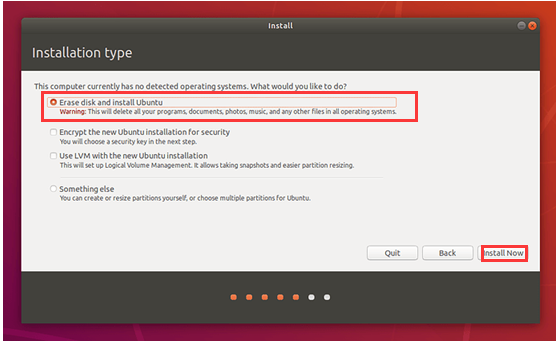
Step 6: Check the Erase disk and install Ubuntu option and click Install now.
Part 5: Set up Ubuntu
After executing the steps above, you will install Ubuntu smoothly. To use Ubuntu, you are required to set up it. Now, follow these steps to do that.
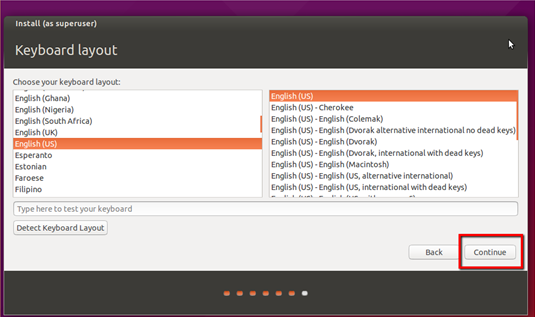
Step 1: You will be prompted with a window after installing Ubuntu. Choose a time zone that matches with your present position and choose the Keyboard layout [ex: English (US)]. Then click Continue to start the process.
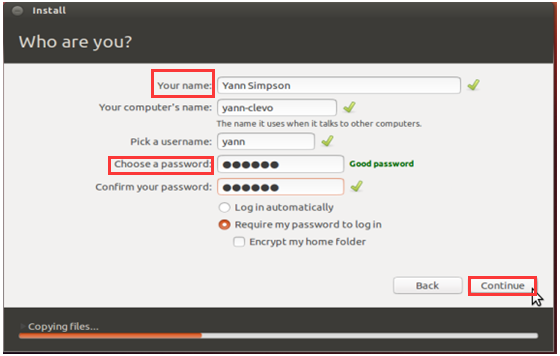
Step 2: In the next window, enter the corresponding information in the proper place such as “Your name”, “password”, “username”, etc. After that, click Continue to go on the process.
Step 3: Now, you need to wait patiently until the finish of the process. Then do as the on-screen instruction to restart the virtual machine. When the VM restarts normally, you can use it. From here, the whole Ubuntu VirtualBox installation process ends.
Conclusion
Up to now, this post introduces all the details of installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox including VirtualBox application, benefits, requirements and steps of installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox. This is a complete guide on How to install Ubuntu on Windows 10 using VirtualBox.
If you have any new thoughts on this topic – how to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox, please share them with us in the comment area. For doubts and questions about MiniTool, you can send us an email via [email protected].
How to Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox FAQ
Here is the tutorial for installing Ubuntu on a virtual machine.
- Open the VirtualBox by double clicking on it.
- Click on New to create a virtual machine.
- Type Ubuntu as the name and choose Linux as the type. Choose the Ubuntu (64-bit) version and click Next to go on. Then follow the prompted instruction to complete the installation.
- To do that, you should firstly choose virtual machine in the main menu of VirtualBox and click on the Settings button.
- Then click Storage tab in the Settings menu. After that, you will see an image of a disk and the word “Empty” under the Controller section.
- Click on Empty and choose the CD/DVD icon. Click Choose a virtual CD/DVD disk file and move to the ISO file that you are going to import to the virtual machine. Do as the prompted instruction to finish the process.
User Comments :