Introduction to Thunderbolt 3 and USB C Ports
What Is USB C Port?
USB-C, short for USB Type-C, is a form of USB hardware interface released by USB-IF in 2014. The biggest feature of its appearance is that its upper and lower ends are exactly the same, no longer distinguishing USB front and back.

USB interface has various hardware interface forms, such as USB Type-A, USB Type-B, Micro-USB, etc. However, USB C is now becoming more and more popular and it seems that USB-C is gradually substituting Micro-USB and USB Type-A. The possible reasons are as follows:
- The size of the USB-C interface is 8.3×2.5 mm, which is smaller than the USB Type-A interface. Therefore, USB C port is taking the place of USB A port in Ultrabooks.
- USB Type-C doesn’t need to distinguish the front and back, which makes it easy to insert. Therefore, it substitutes the Micro-USB port.
Further Reading:
When it comes to USB C vs other USB hardware ports, some people may think of USB 3.x, Power Delivery, etc. Actually, these factors have nothing to do with USB C. For example, many phones’ Type-C ports still use USB 2.0, while USB A ports support USB 3.x and PD protocol, too.
The only thing that USB C is better than USB A is that it is flippable (you don’t need to distinguish its upper and lower ends when inserting it). Due this point, USB-IF and manufacturers decide to abandon USB A. As a result, USB PD 3.0, partial USB 3.x (e.g. USB 3.2 Gen1x2, USB 3.2 Gen2, etc.), and USB4 have decided to deprecate the USB A port.
If you want to learn about these USB hardware interface forms, you can read this post: USB Types and Speeds [An Overall Introduction with Pictures].
What Is Thunderbolt 3?
Thunderbolt interface is the brand name of an external interface developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple. This interface combines PCI Express data transmission technology with DisplayPort display technology, so that it can transmit data and video signals at the same time.
So far, the Thunderbolt interface has three generations:
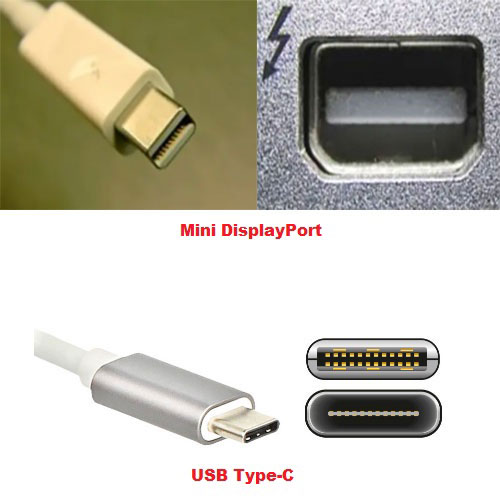
- Thunderbolt 1: It is based on Mini DisplayPort and PCI-E 2.0 X2, supports full duplex (supporting sending and receiving data at the same time), and offers a bandwidth of 10Gbps.
- Thunderbolt 2: It is based on Mini DisplayPort and PCI-E 2.0 X4, supports full duplex, and offers a bandwidth of 20Gbps.
- Thunderbolt 3: It is based on USB Type-C port, uses PCIe 3.0 X4, supports full duplex, and offers a bandwidth of 40Gbps (3.94 GB/s).

To figure out what Thunderbolt 3 is, you should learn about the following 3 aspects:
1. What is the Thunderbolt port used for?
Thunderbolt 3 port has the following usage:
- It can serve as a USB port to transfer data between computer and peripheral devices. In addition, it is backward compatible with USB 3.0 and 2.0.
- It can serve as a DisplayPort to transfer audio and video signals. Therefore, you can use it to connect an external GPU or a Display screen.
- It can be used to connect a docking station, thus extending external port.
2. Mini DisplayPort vs Thunderbolt
Will Mini DisplayPort be replaced by Thunderbolt interface? Some people may be curious about this problem. In this part, I will explain Mini DisplayPort vs Thunderbolt to you.
To figure out Mini DisplayPort vs Thunderbolt, you should know that Thunderbolt is a hardware interface like USB C, while Mini DisplayPort is more like DisplayPort interface. Mini DisplayPort is the micro version of DisplayPort interface.
DisplayPort is a display interface issued by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). This interface can be used for both internal display connection and external display connection. The latest DP version is DisplayPort 2.0 standard that was released in 2019.
DP 2.0 uses Thunderbolt 3 as the physical interface (PHY). The Thunderbolt 3 port’s bandwidth is 40Gbps (in full duplex mode). But display ports don’t need full duplex mode (it just needs one end to send and the other end to receive signals). Therefore, DP 2.0 merges the bidirectional channels into a unidirectional channel, reaching a unidirectional bandwidth of 80Gbps.
DP 2.0 will support USB C interface. DP Alt Mode on USB Type-C allows USB Type-C to achieve the display effect of DP 2.0. As for Thunderbolt 3 (just like the Thunderbolt Alt Mode on the USB C interface), part of it to be used for data transmission, and only half of it is used for display output, so its display effect is only half of DP 2.0.
3. Thunderbolt 2 vs 3
Thunderbolt 3 is so popular nowadays, but the previous Thunderbolt 1 and 2 are not so famous. Some people may be curious about Thunderbolt 2 vs 3. The differences between them are as follows:
- Hardware Interface: Thunderbolt 2 uses Mini DisplayPort while Thunderbolt 3 uses USB Type-C.
- Performance: Thunderbolt 2 is based on PCI-E 2.0 X2 and offers a bandwidth of 10Gbps, while Thunderbolt 3 is based on PCI-E 3.0 X4 and offers a bandwidth of 40Gbps
- Technical Copyright: Since 2018, Intel has completely waived the technical authorization fee for the Thunderbolt 3 interface. From then on, Thunderbolt 3 is becoming more and more popular.
PCI vs PCIe: What’s the Difference and How to Distinguish Them?
Thunderbolt 3 vs USB C
Is USB C the same as Thunderbolt? What about USB C vs Thunderbolt or Thunderbolt vs USB C? Some people may ask those questions. But I think the real question they want to ask is “Is USB C the same as Thunderbolt 3?” and “What about USB C vs Thunderbolt 3 or Thunderbolt 3 vs USB C?”
Then, is Thunderbolt 3 the same as USB C? Apparently, Thunderbolt 3 is different from USB C, although the Thunderbolt 3 interface will use the USB C hardware port. The relationship between Thunderbolt 3 and USB C can be well embodied in the following analogy:
If we compare the interface to a sandwich, the Thunderbolt 3 is just like the main ingredient (like chicken, beef, etc.) and the USB C is like the bread in the sandwich. The main ingredient can be replaced as your will. Of course, the Thunderbolt 3 can also be replaced by other Buses like USB 3.x. However, the bread (USB C) is relatively fixed, and it is used to wrap all the ingredients.
To make you understand USB C vs Thunderbolt 3 better, I will explain their difference from the following 2 aspects:
1. Speed
USB C port’s speed depends on the Bus it uses. If it uses USB 2.0, its speed is the speed of USB 2.0. If it uses Thunderbolt 3, its speed is the speed of Thunderbolt 3.
As for Thunderbolt 3, it has three versions: Double Port (DP) version uses a PCIe 3.0 ×4 link to provide two Thunderbolt 3 ports (DSL6540, JHL6540, JHL7540); Single Port (SP) version uses a PCIe 3.0 ×4 link to provide one Thunderbolt 3 port (DSL6340, JHL6340, JHL7340); Low Power (LP) version uses a PCIe 3.0 ×2 link to provide one Thunderbolt 3 port (JHL6240).
Apparently, Thunderbolt 3 ports offered by DP and LP versions are 20 Gbps, and SP offers 40Gbps Thunderbolt 3 ports.
2. Functionalities
When it comes to USB C ports, some people will say they feature not only high speed, but also powerful functionalities like Power Delivery and Display Port Protocols. USB PD allows USB C port to deliver power up to 100W and DP protocol allows it to transmit audio and video signals.
However, have to face the fact that these features (or protocols) are not standard for USB C ports. Only a few advanced USB C ports may integrate PD and DP protocols to achieve fast charging and video transmission features.
As for Thunderbolt 3 interface, it must have DisplayPort feature, according to its standard. But the USD PD is optional. It can be said that the Thunderbolt 3 interface is the top-level presentation of the USB Type-C interface.
Benchmark Thunderbolt 3 and USB C Drives
Nowadays, more and more laptops are equipped with Thunderbolt 3 or USB C interfaces. To determine whether the port on your laptop is a Thunderbolt 3 port or an ordinary USB C port, the simplest way is to see whether there is a lighting mark beside the port.

Then, you may need to buy a compatible external hard drive or flash drive for the port. If so, you can refer to the following two posts:
- What Is a Thunderbolt Hard Drive? Which Is the Best?
- An Introduction to Choosing Best USB-C Thumb Drives in 2020.
After buying the Thunderbolt 3 or USB C drives, I recommend you to benchmark them on your computer to see whether they can run as fast as expected. To benchmark them, You can try MiniTool Partition Wizard whose Benchmark feature is totally free. Please refer to the following tutorial:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Click the above button to free download MiniTool Partition Wizard. Launch this software and go to its main interface. Then click Disk Benchmark on the toolbar.
Step 2: Select the Thunderbolt or USB C drive and set parameters to test the disk performance.
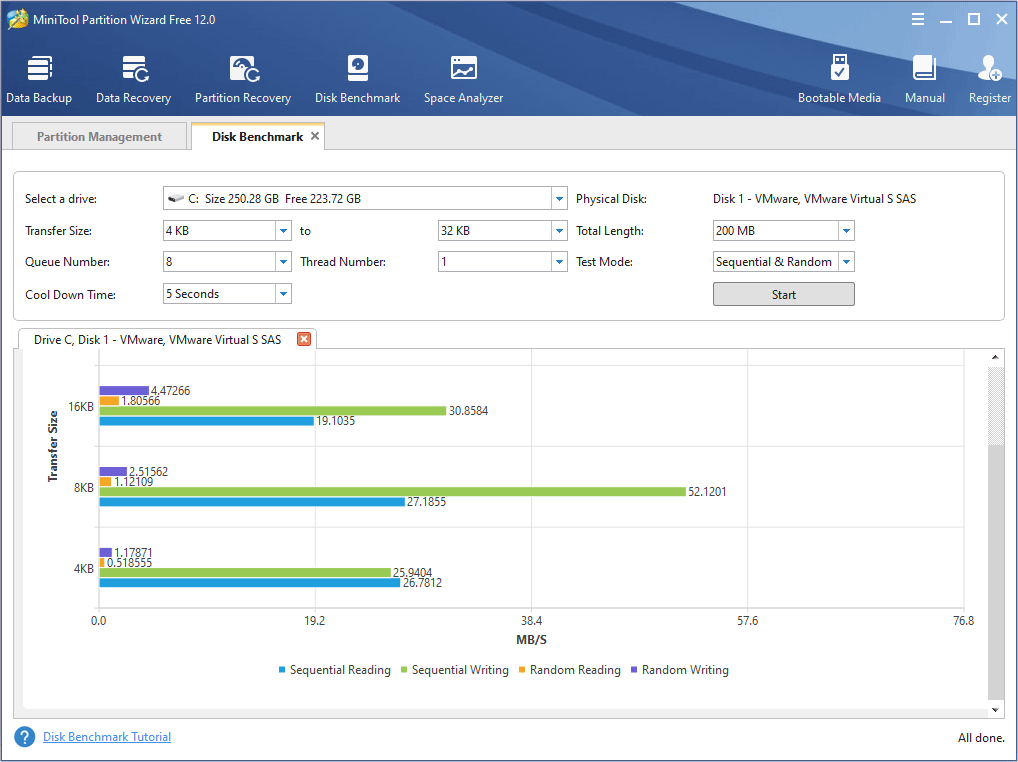
Step 3: Click Start after the parameters are set. Then, wait seconds to get a disk performance test result. If the result is not satisfactory, it is recommended to consult the drive seller.
Bottom Line
Does this post help you learn about Thunderbolt 3 vs USB C better? Do you have different idea about this topic? Anyway, please give us your feedback in the following comment zone. Besides, if you have difficulty in benchmarking drives, please contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Thunderbolt 3 vs USB C FAQ
Thunderbolt is not the same as USB C. First, USB C is just a form of USB hardware interface, while Thunderbolt is an interface standard combining PCI Express data transmission technology with DisplayPort display technology.
Second, Thunderbolt has three versions and only Thunderbolt 3 uses USB C port. Last but not least, USB C port doesn’t mean a Thunderbolt 2 interface. It is probably a USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, or USB4 interface.
User Comments :