There are usually lots of sensitive data kept in your computer’s SMM. Like other data, they may get lost or damaged suddenly due to different reasons. Therefore, this article analyzes the possibility and steps to recover data from SMM mode. You’re advised to ask MiniTool for help when encountering disk problems.
A New Variation of Spectre Attack Allows Attackers to Recover Data from SMM Mode
A new variation of the Spectre attack was designed by the experts and researchers from Eclypsium a year ago. The new application of speculative execution attacks is able to avoid the hardware-based memory protections. So it is able to give access to the attackers to recover data that have been kept in CPU’s System Management Mode.
Back to 2017, it was Jann Horn from Google Project Zero & other security researchers who first discover the vulnerabilities that will have impact on the modern processor architectures’ speculative execution process.
A Public Proof-of-concept Code Was Modified
As you know, the public proof-of-concept codes were designed and released for the Spectre variant 1 (CVE-2017-5753) vulnerability. It is reported in a previous research that one of the codes was changed by the Eclypsium team.
What’s the purpose of modifying the public proof-of-concept codes?
- To get rid of the SMRR protection mechanism.
- To access the content kept in the System Management RAM (SMRAM).
Please note: SMRAM refers to the physical memory in which the working data is saved and run by SMM.
SMM Code and Data Are Disclosed
Because SMM generally has privileged access to physical memory, including memory isolated from operating systems, our research demonstrates that Spectre-based attacks can reveal other secrets in memory (eg. hypervisor, operating system, or application).– said the Eclypsium team
These enhanced Spectre attacks allow an unprivileged attacker to read the contents of memory, including memory that should be protected by the range registers, such as SMM memory. This can expose SMM code and data that was intended to be confidential, revealing other SMM vulnerabilities as well as secrets stored in SMM.– said the researchers
The kernel-level PoC exploit provides access to different hardware interfaces, which gives attackers better control over the system hardware and access to different hardware interfaces such as physical memory, IO, PCI, and MMIO interfaces. It also provides access to interfaces at a higher privilege level, such as software SMI.– explained the researchers
In addition, the researchers said they will integrate the PoC exploit into CHIPSEC for the sake of expanding their tests in the future.
The enhanced Spectre attacks make it possible for even unprivileged attackers to get access to the contents of memory including SMM memory, which is expected to get protection by range registers. In this way, the top-secret SMM code and data will be revealed. As a result, the related SMM vulnerabilities and secrets stored in this area will also be leaked.
All in all, changing one of the public proof-of-concept codes designed for the Spectre variant 1 (CVE-2017-5753) vulnerability has contributed to the discovery of SMRAM and SMM data. And according to the Eclypsium team, this may be used to discover more data (not only SMM related data) from physical memory in the future.
How to Recover Data from Internal Memory
The Eclypsium researchers have explained the way they used to recover data from SMM mode. In this section, I will show you how to recover files from the internal storage of your PC when system crashes.
Step 1: create a bootable disk (CD/DVD/USB flash drive).
- Get a license that has a snap-in WinPE Bootable Builder.
- Launch MiniTool Power Data Recovery and register it with the license.
- Connect a USB stick or insert a CD/DVD to the computer.
- Click on the Bootable Media button at the bottom left.
- Select WinPE-based media with MiniTool plug-in.
- Choose a media destination (ISO File, USB Flash Disk, or CD/DVD Writer).
- Click Yes in the pop-up window to confirm and wait for the disk building process.
- Click Finish and remove/disconnect the bootable disk from computer.
Step 2: change boot sequent in BIOS.
- Connect the bootable disk to the device that runs into problem and restart it.
- Press F10, F2, F12, F1, DEL, or another button to access BIOS.
- Use the arrow keys on the keyboard to select the Boot tab (the feature name may be different, but its function is organizing boot sequence).
- Also, use the arrow keys to set the bootable disk as the first boot device.
- Save changes and exit BIOS.
How to fix if your PC can’t boot after BIOS update.
Step 3: scan the internal drive and recover files from it.
- Follow the on-screen instructions until you enter the MiniTool PE Loader window.
- Select the first option to launch MiniTool Power Data Recovery when PC won’t boot.
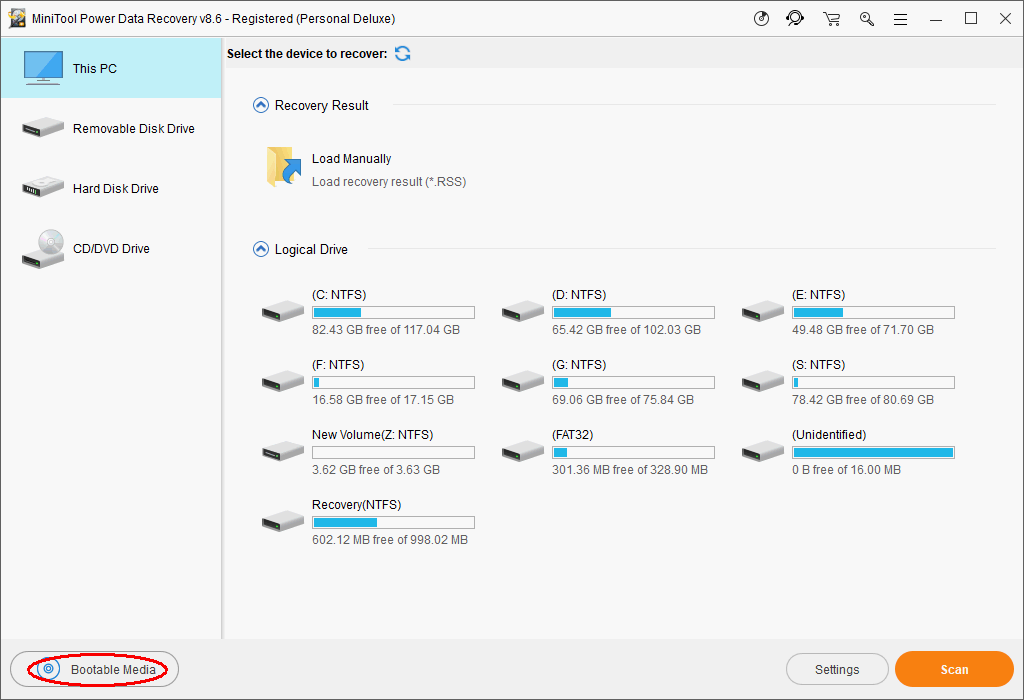
- Choose Hard Disk Drive from the left sidebar and double click on the internal disk from the right.
- Wait for the disk scan process and look through the found data carefully.
- If you find the files you need, please select then and click Save; if you don’t, just wait for the completion of the scan and then do this step.
- Select a directory to save files; you should choose an external device (please connect the removable drive with enough free space to the computer before this step).
- Click on the OK button to confirm your selection and wait for the recovery to complete itself.
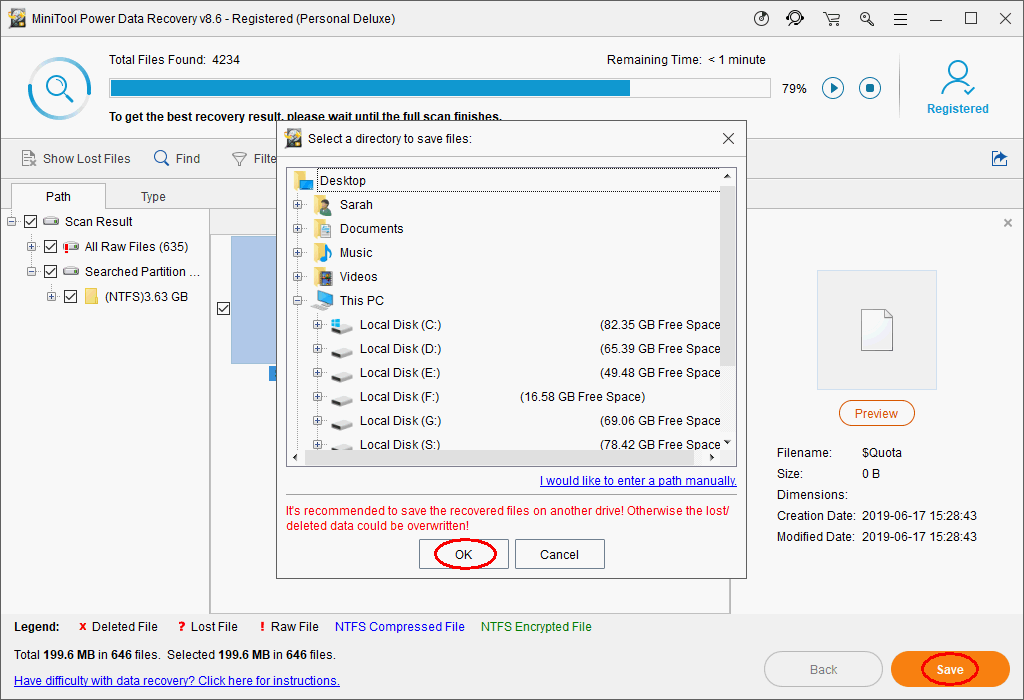
Please note: when the recovery is finished, a prompt window will show up in the software to inform you (Congratulations! The select files have been saved to *). You should click OK and try useful solutions to repair the unbootable computer.
If you doubt about this program, please use the trial edition first.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
What Is SMM in Computer
The full name of SMM is System Management Mode; it is also called ring -2 in reference to protection rings. In the early 90s of last century, the SMM was firstly introduced with the Intel 386SL. To be precise, SMM is an operating mode of the x86 central processor units. It is a sensitive area on your computer which is highly protected by the CPU (Central Processing Unit).
Your operating system will be suspended whenever SMM receives a code. In the meantime, various commands will be run by the UEFI/BIOS firmware to gain enough elevated privileges and get the access to all the hardware and data.
What happens during the interrupts?
- The operating system will be suspended.
- The firmware-specific code will be executed.
- The system hardware control, power management, and proprietary OEM code will be controlled.
In short, your hardware will run smoothly and all the software included will run.
Contained in the firmware or a hardware-assisted debugger, the SMM works as an alternate software system. You can only access and execute the System Management Mode when you get high privileges.
The SMM is so important that anyone is not allowed to access it for both maintenance and security reasons.
Features of SMM
The System Management Mode has 3 main attributes:
- It is in fact a 16-bit mode (x86 processor mode), which can’t be accessed or interrupted by the highly-privileged software.
- It is used to control motherboard and manage power, such as thermal management and power management on laptops. This is also known as ACPI.
- It can be accessed only when the computer CPU receives a hardware System Management Interrupt (SMI).
SMM memory:
After entering, each CPU register will be kept to a memory saved state map, which is located in a memory zone called SMRAM. So where is the SMRAM? In fact, it is contained in the computer’s RAM. What’s the function of SMRAM? It is capable of executing SMI handler.
The CPU state will be recovered from the map saved in memory when the rsm assembly language instruction runs by SMI handler. You should realize that there is no notification when operating system is interrupted by any management software running in SMM of PC.
SMRAM Security Model & Mechanism
The SMM code is only able to run on the platform with full privileges (which are even more than the operating system kernels).
Should SMRAM be accessed all the time?
Of course not. The SMRAM should be accessed when the system is contained in SMM. In other cases, the access should be prevented, making it only possible for SMI handler to modify its content.
In summary, the key point is whether the D_OPEN bit is set in the chipset or not.
- If it is set, SMRAM can be accessed.
- If not, the legacy, TSEG, and high SMRAM can only be accessed when the CPU is in System Management Mode.
What about the protection mechanism?
In fact, the D_LCK bit is used as the main mechanism to prevent modifying SMI handler. When the D_LCK bit is set, the configuration bits for the SMRAM will turn into read only state (D_OPEN bit included). If you ask me where the configuration bits are, they are located in the chipset.
How to Protect the SMM Mode
According to the researchers from Eclypsium team, they have sent the new Spectre attack variation discovered by them to Intel in March, 2018. And Intel’s response to this issue is get the original patches of Spectre variant 1 and variant 2. They said this would be enough to stop the attack chain.
We have reviewed Eclypsium’s research and, as noted in their blog, we believe that the existing guidance for mitigating Variant 1 and Variant 2 will be similarly effective at mitigating these scenarios. We value our partnership with the research community and are appreciative of Eclypsium’s work in this area.– said a spokesperson of Intel
In fact, a report from Eclypsium discuss deeper on the attack.
Eclypsium Team’s Future Research
According to Eclypsium Team, the PoC is only tested against SMRR (System Management Range Registers). However, by virtue of other hardware-based range register protection mechanisms, a similar attack may work against the memory.
SMM security mitigation:
In March, 2018, Intel advise us to integrate the same software guidance to SMM in order to migrate Spectre variant 1. As a result, the Spectre variant 1 should be migrated by using LFENCE instructions. When it comes to the firmware from different system manufacturers or independent BIOS vendors, it is also suitable.
In addition, the mitigations have also been introduced to other Spectre attacks by the vendors.
Software executed before a system management interrupt (SMI) cannot control the predicted targets of indirect branches executed in system management mode (SMM) after the SMI.– according to Intel’s Speculative Execution Side Channel Mitigations document
Another useful strategy may be using firmware to limit the access of SMM to memory. For most firmware, it will map the physical memory to SMM’s page table. The latest version of Tianocore is an exception; it only map the necessary parts of memory into the page table. Hence, the influence will be decreased greatly. The fact is that most of the current systems are made on the basis of an older version of Tianocore. Therefore, it is suggested that firmware developers should keep this feature in the later versions. This is significant for protecting users from current and other SMM vulnerabilities.
Final Words
After reading above content, you know system management mode (SMM) is a very important unit on your computer; it stores much confidential information that is not expected to be available for common users. However, researchers found a new variation of Spectre Attack can allow the access to SMM, resulting in security problems. This post tells you how to recover data from SMM mode and how to protect the SMM memory effectively.
User Comments :