What is direct attached storage (DAS)? What is the best direct-attached storage solution? SAN vs NAS vs DAS: what’s the difference? How can you back up data to DAS? This comprehensive guide from MiniTool covers everything you want to know.
Data storage is a critical element since it can ensure the security of files and other data in the event of system crashes, natural disasters, cyber attacks, and more. When needed, you can easily access the stored data. Today, let’s focus on a special storage type, namely, direct attached storage.
What Is Direct Attached Storage
Direct attached storage, also known as DAS, refers to a type of storage directly attached to a computer, workstation, or server without going through a network. DAS can be divided into 2 categories: internal and external storage.
Internal DAS includes hard drives or SSDs that are directly installed in a computer. That is, desktops, laptops, and servers use an internal HDD or SSD. Those devices belong to a form of DAS. External DAS refers to storage devices such as external hard drives, USB flash drives, and SSDs, as well as drive enclosures (like RAID arrays) connected to a computer via a cable.
Usually, an external DAS device creates a direct connection to a computer or server through interfaces like universal serial bus (USB), eSATA, SAS, SATA, SCSI, etc. Technically, optical storage devices (CD/DVD) and tapes are DAS devices since they are connected to a computer. But we usually refer to HDDs, SSDs, and USB drives.
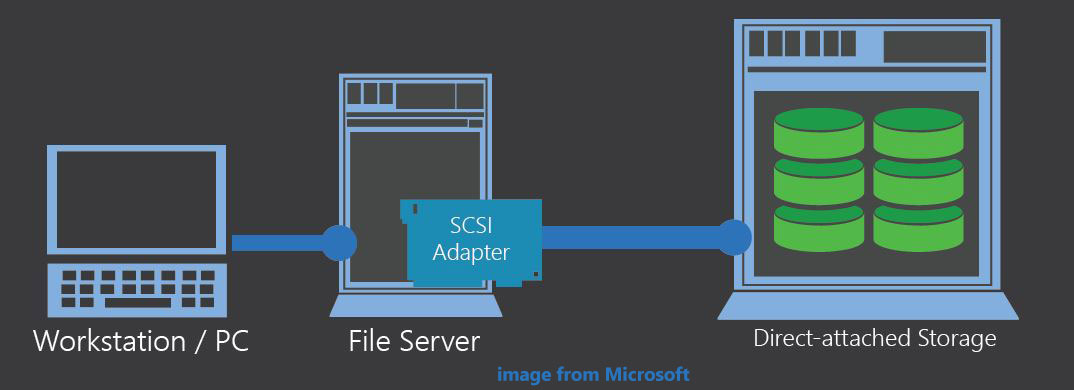
Since a direct attached storage device is connected directly either internally or externally, only the host computer can access the data directly. If other devices want to access data, they must go through the host computer.
What Is Direct-Attached Storage Used for
What is the use of a DAS device? Here are the details.
- Primary, DAS is used as the local data storage device, offering high-speed data storage capability for a single server or computer.
- Direct attached storage can serve as a straightforward data backup solution. You can store important file copies to it through a direct connection, achieving faster backup and recovery, and ensuring data reliability and integrity.
- For individual users and SMBs (small to medium-sized businesses) that need simple, high-performance, and dedicated storage, without the need to share data across the organization, DAS is a cost-effective solution.
- In larger enterprises for specific applications, DAS is a choice.
- DAS can serve as private storage connected to dedicated servers in data centers.
In short, direct-attached storage devices are practical choices and play a crucial role for businesses and individuals.
Pros and Cons of DAS
A coin has two sides. Similarly, direct attached storage has advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore them in detail.
Advantages
DAS excels in speed & efficiency, setup, and cost.
- High performance: It offers fast access to data since it is directly attached to the computer, eliminating work congestion issues. This is why your business uses DAS for applications requiring high-speed data retrieval and low latency, such as video editing.
- Ease of use: Direct attached storage features simplicity and ease of setup. Internal DAS is ready to use as the DAS device is part of the computer, while external DAS devices are plug-and-play, usually connected via USB ports. Even though you have limited computer skills, you can easily set up DAS.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to other storage solutions, DAS is cost-effective. It doesn’t need additional hardware or software to run, but requires hard drives or drive enclosures. For individuals and small businesses, it is a budget-friendly option.
Disadvantages
In some aspects, direct attached storage has limitations, as shown:
- Limited scalability: The storage space of DAS devices is finite. As data grows over time, you may need to add many drives, which is cumbersome and costly.
- Poor flexibility: DAS devices are connected to specific computers, restricting the way you share data with other users or systems.
- Lack of centralized management: One host computer manages the DAS systems, and any access from outside that computer is limited. This means you need to manage each DAS device, making centralized management difficult.
- Potential for data loss: Once the host computer or server goes wrong, direct-attached storage devices are subject to hardware failures, leading to data loss.
How DAS Handles Data Security
To a great degree, the security of direct attached storage relies on the host system. As stated above, it is directly connected to a server or computer, meaning its security is tied to that host device. Data on the DAS device is at risk if the host computer is compromised.
So, to enhance security, you can implement some measures on the host system.
#1. Perform strong access controls
It is necessary to create strong and individual passwords for all storage devices. The password had better have a minimum of eight characters, including a number and a special character like #, @, etc. Besides, administrators should implement access controls for all apps that use DAS. Only approved users can view or manage files on the DAS device.
#2. Regularly update software and systems
Outdated systems or software are vulnerable to attacks. Keeping them up-to-date helps protect against various attacks.
#3. Secure all physical premises
It is important to secure the physical places where the host computer and DAS are located, including server rooms and data centers.
#4. Encrypt DAS data
Data encryption effectively protects your direct-attached storage from unauthorized access. Even though the device is stolen, nobody can access the data without permission.
Best Direct Attached Storage Solution
The best DAS solution should satisfy your needs. As mentioned above, DAS solutions include various storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs) and some direct attached storage enclosures.
Which DAS Drive to Choose?
Here are some factors you should consider.
- Storage capacity: Make sure how much storage space you need based on the data storage requirements.
- Performance: Compare HDDs and SSDs and determine which one to use. For speed, use an HDD. For capacity, choose an HDD. Or use both an SSD and an HDD as the DAS devices. Learn the differences between these two disk types in this guide on SSD vs HDD.
- Connectivity: Ensure the DAS device is compatible with your computer. Usually, select the one that uses the interface like USB, eSATA, or Thunderbolt.
- Budget: Since DAS solutions vary in price, select the one that fits your budget. Generally, external hard drives are cheaper than SSDs, while RAID arrays and enclosures have a high cost.
- Use Case: Depending on the intended use, choose a proper direct-attach storage device. For example, purchase Thunderbolt DAS if you demand fast local access for video editing.
Examples of DAS Manufacturers
Many manufacturers offer a variety of types of direct-attached storage devices, as follows:
LaCie: Lacie d2 Professional and the 2big series
OWC: OWC ThunderBay 8 Thunderbolt 3 Storage Enclosure
QNAP: QNAP TR-004 4 Bay USB Type-C Direct Attached Storage
Water Panther: WP Arsenal DAS Drives
Western Digital (WD): WD Red Pro
SAN vs NAS vs DAS: What’s the Difference
Now we have introduced much information about direct attached storage, DAS. In addition to DAS, you may have heard another two storage types, such as SAN and NAS.
SAN
SAN, short for storage area network, is a dedicated and high-speed network that offers block-level access to storage devices. Usually, it is used in enterprise environments to centralize storage and share storage resources among multiple servers. It has three main features such as high performance, low latency, and efficient data access.
NAS
NAS, also known as network-attached storage, refers to a dedicated file storage device that connects to a network. Multiple users can share and access files over a network. Essentially, NAS acts as a private cloud, offering the capabilities of convenient data storage, management, and sharing within a LAN (local area network).
NAS vs DAS vs SAN
Which one to choose from these three storage types? Here is a comparison table for you to make a choice easily.
| DAS | NAS | SAN |
| Directly connected to a host computer or server | Connected to a network via Ethernet | Connected to servers using Fibre Channel or Ethernet connections |
| Cheaptest | Less expensive | More expensive |
| High performance | Limited performance by the network (high latency) | Highest performance |
| Least scalability | Moderately scalability | Highly scalablility |
| Simplest to set up and manage | More difficult | Most complex to implement and manage |
| Used by smaller businesses or individuals. | Used by SMBs (small to medium-sized businesses) | Used by larger businesses and corporations |
To know more information, refer to our previous posts on NAS vs DAS and SAN vs NAS.
How to Back up to DAS
Direct-attached storage is a good option for backups due to the faster backup and retrieval times. So, how to backup to DAS? You can directly connect a DAS device to your computer via USB or another interface and perform the backup operation.
For DAS backup, we recommend MiniTool ShadowMaker. Compatible with Windows 11/10/8/7 and Server 2022/2019/2016, this backup software provides the best backup and recovery solution. It supports backup files, folders, disks, partitions or Windows systems to various locations, such as external hard drives, SSDs, HDDs, NAS, DAS, etc.
Importantly, MiniTool ShadowMaker allows you to create automatic backups by configuring a plan like daily, weekly, monthly, or on an event. Besides, you can back up only the changed data by setting the incremental or differential backup scheme meanwhile deleting old backup versions.
Take these steps for DAS backup:
Step 1: Connect your DAS device to a computer via a cable.
Step 2: Download, install, and launch MiniTool ShadowMaker Trial Edition (30-day free trial).
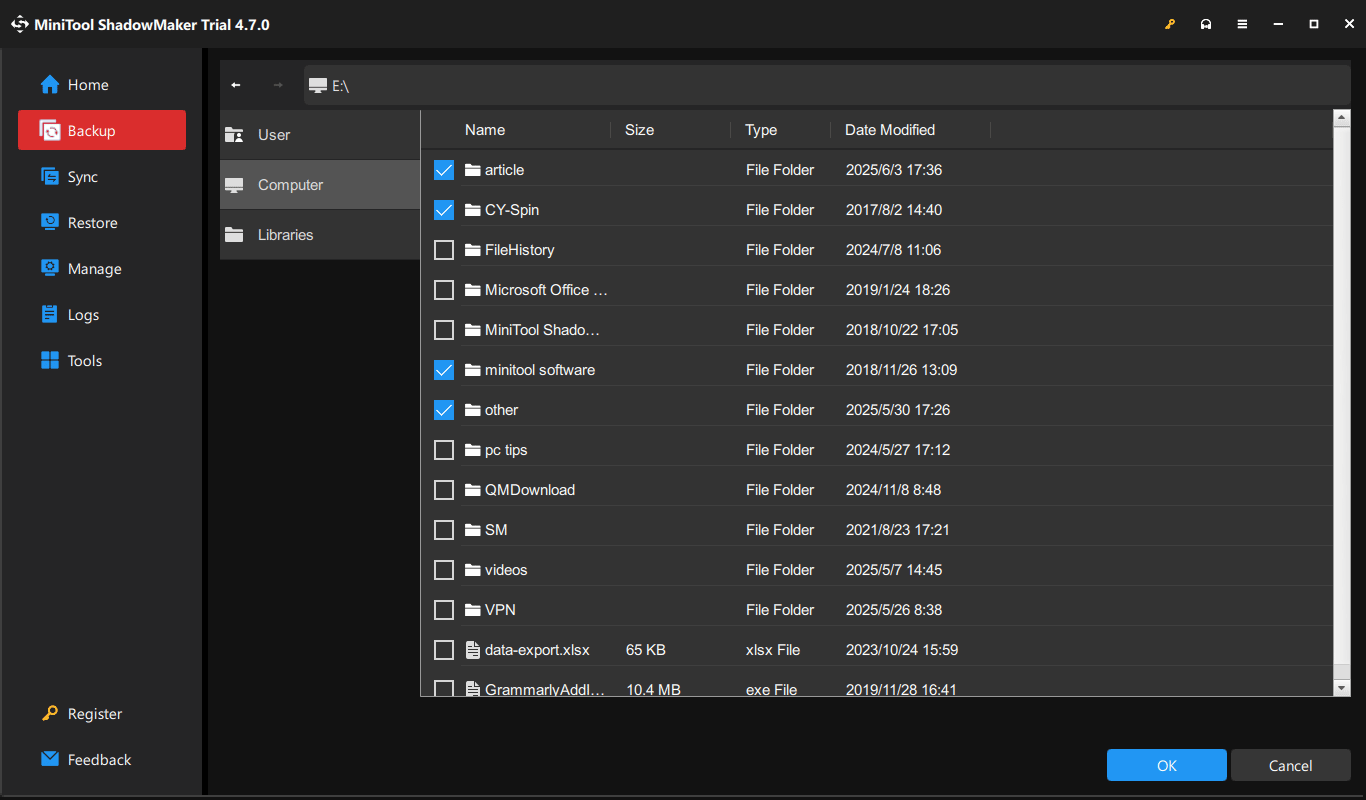
Step 3: Head to its Backup tab. Then, choose the files or folders you want to backup to DAS by navigating to SOURCE > Folders and Files.
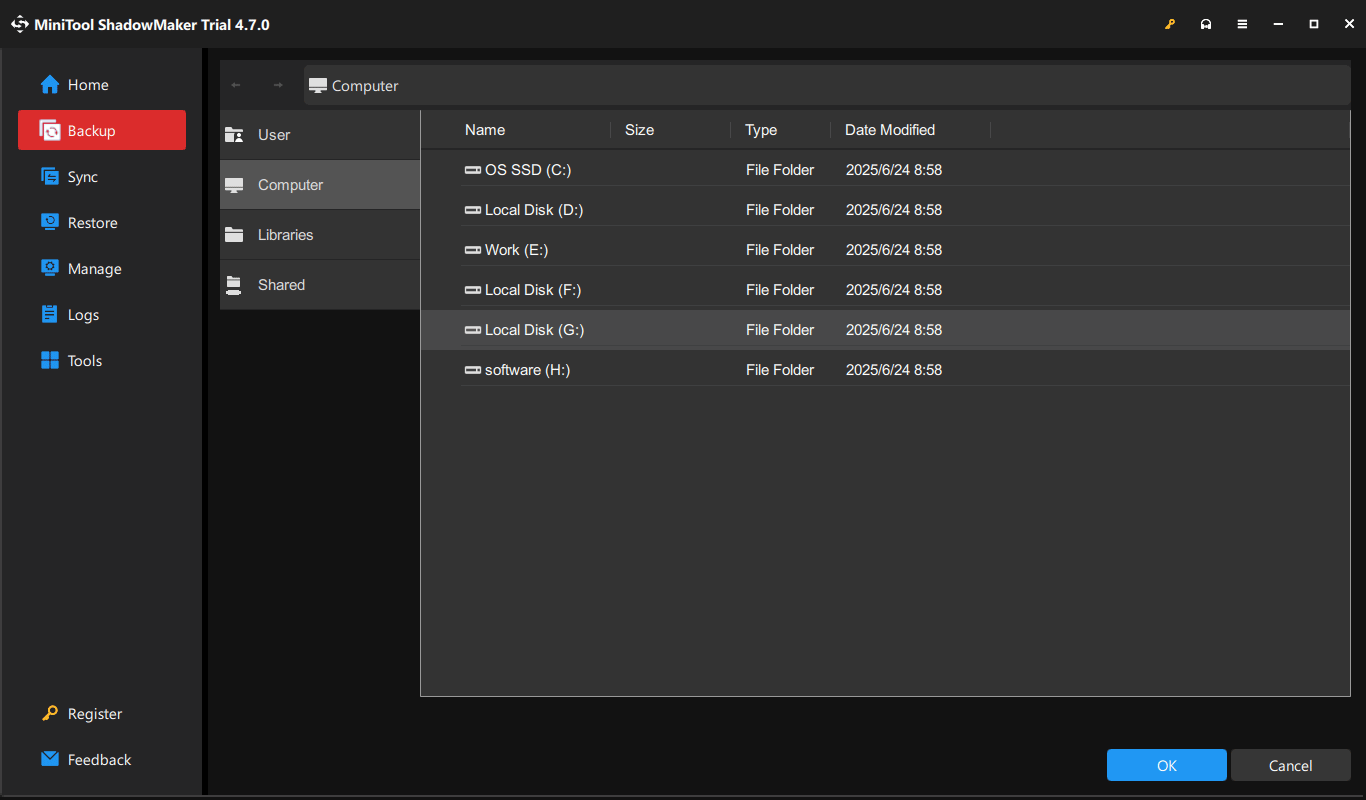
Step 4: Select your DAS device as the target path by hitting DESTINATION > Computer.
Step 5: Begin the backup process by clicking Back Up Now.
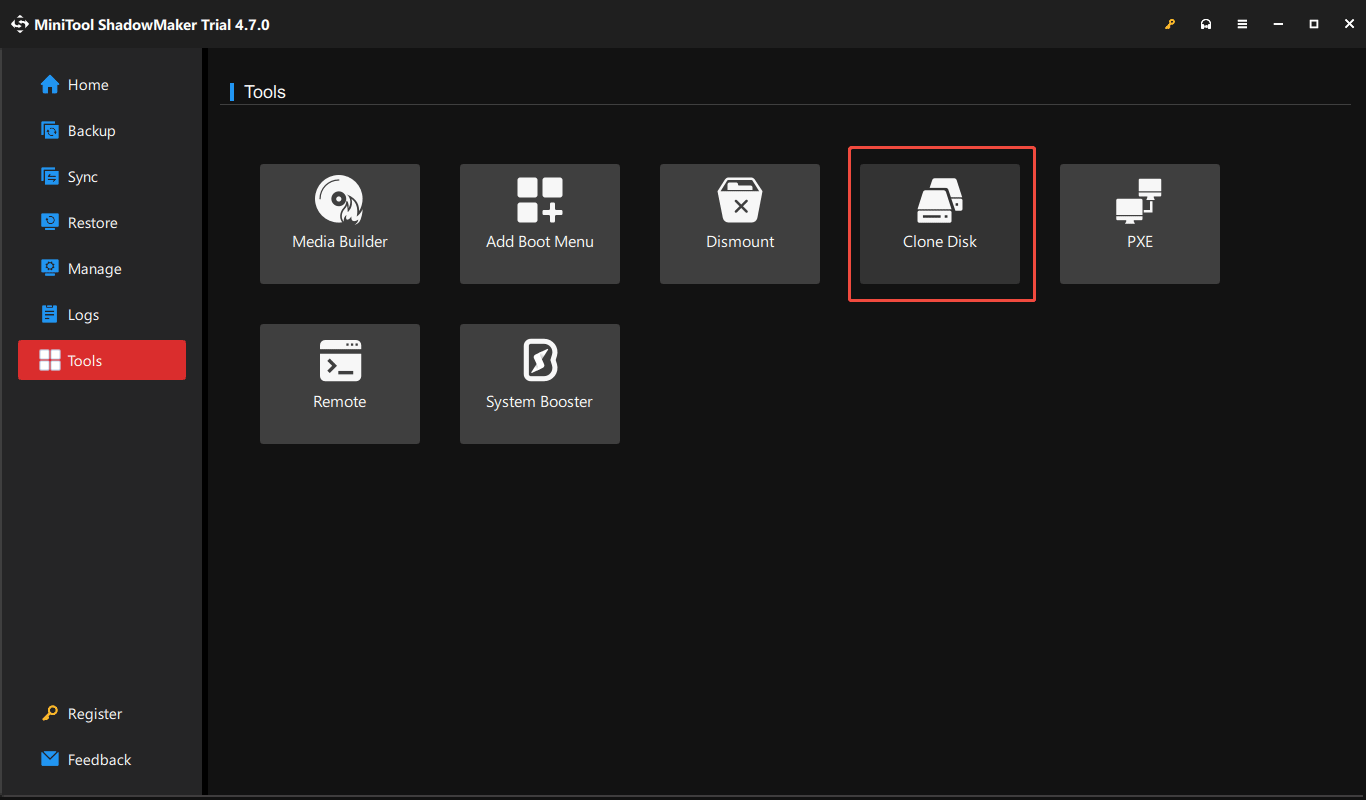
Besides, you can clone your entire system drive to the direct attached storage device for a complete backup. MiniTool ShadowMaker also comes in handy. As hard drive cloning software, it comes with the Clone Disk feature, cloning HDD to SSD, smaller SSD to larger SSD, USB to USB, SD card to SD card, etc., with ease.
Just access the Tools tab, click Clone Disk, select the system drive as the source drive, choose the DAS device as the target drive, and begin the cloning process. Learn more information from this tutorial on how to clone a hard drive.
Bottom Line
Direct attached storage is a reliable, practical, and economical storage solution. Although it has some limitations, for small businesses and individuals, it is still a good choice because of its simplicity, ease of use and high performance.
Just select the best DAS solution as per your budget and run MiniTool ShadowMaker to create DAS backup to keep computer data secure.
This post covers much information about DAS and we hope it helps you much. If you have any suggestions or questions on our product, welcome to contact us.


User Comments :