SAS hard drives are generally used in RAID to store and manage data. However, even though RAID has a certain degree of fault tolerance, data loss in SAS hard drives still occurs from time to time. This MiniTool article will explore the causes of data loss and provide a guide for SAS hard drive recovery.
In the following sections, I will introduce you to the relevant information about SAS hard drives and RAID so that you can have a better understanding of them.
About the SAS Hard Drive
A hard drive is a non-volatile storage device used to store digital data, which is an integral part of modern computing devices. Hard drives are divided into three main categories: solid state drive (SSD), hard disk drive (HDD), and solid state hybrid drive (SSHD). Furthermore, hard drives can also be divided according to interfaces, and SAS is one of them.
What is the SAS interface? SAS (Serial Attached SCSI Interface) is a high-performance interface technology used to connect storage devices (such as hard disks and solid-state drives). It inherits the reliability of the traditional SCSI interface and adopts serial transmission, which greatly improves the data transmission efficiency.
What is a SAS hard drive? A SAS hard drive (Serial Attached SCSI Hard Drive) is a high-performance hard drive using the SAS interface, which is widely used in enterprise-level servers and storage systems. It combines the high reliability of SCSI technology and the high transmission efficiency of serial connection to meet the storage needs of critical missions. The following content introduces its types and some features.
Types of SAS hard drives:
- SAS HDD (mechanical hard drive): It provides large-capacity storage, usually used to store frequently accessed data.
- SAS SSD (solid-state drive): It provides faster read and write speeds, suitable for high-performance applications.
Features of SAS hard drives:
- High performance. Common rotation speeds are 10,000 RPM or 15,000 RPM, suitable for high-frequency read and write tasks. The transmission speed can reach up to 22 Gbps.
- Dual port support. The dual-port design allows two hosts to be connected simultaneously, supporting multipath redundancy.
- High compatibility. SAS hard drives are backward compatible with SATA hard drives, and SAS controllers can manage both types of hard drives at the same time.
- Stability and reliability. It can run high-load work continuously (24×7) and maintain reliable performance in extreme temperature and vibration environments.
About the RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage technology that combines multiple hard disks to form an array to improve performance, capacity, or data reliability. RAID can include different levels (such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, etc.), and its main function is to optimize data storage and protection.
SAS hard drives are usually the preferred hardware for RAID arrays due to their high performance and high reliability. RAID technology achieves data redundancy and performance improvement by combining multiple hard disks. However, even the most secure devices may face data loss. If you are also wondering how to recover lost SAS hard disk data, then it is recommended that you continue reading this article.
Why Data Loss Happens on RAID-Configured SAS Hard Drives
Although RAID can better protect data to a certain extent, SAS hard drives configured with RAID can still lose data. The following are common causes of data loss, including hardware failure and logical error:
- Hard drive failure: A mechanical failure of the hard drive, such as a damaged head or bad sectors on the disk.
- RAID controller failure: When the hardware RAID controller card or the RAID controller on the motherboard fails, it may make the array unusable and unrecognizable to the operating system, causing data to be inaccessible.
- File system damage: The file system of a RAID array may be damaged due to virus attacks, system crashes, software errors, etc., making data inaccessible.
- RAID configuration loss: RAID metadata or configuration files are damaged, making the array unrecognizable.
- Human error: Accidental deletion, formatting, virus attacks, data write errors, or incorrect reconstruction of the RAID array.
- Power problems: A power outage or voltage fluctuation may damage the hard drive.
- Environmental factors: Extreme temperature, humidity, or physical disasters (such as fire or flood) may damage the hardware.
Before recovery, do not perform any writing operations on the hard disk to prevent data overwriting.
How to Do a RAID-Configured SAS Hard Drive Recovery
If the data loss is caused by physical damage, it will be difficult to recover. You can try to seek professional help. However, if the data loss was caused by a logical failure, it is possible to recover data from the drive. The recovery method depends on the cause of data loss.
Scenario 1. Data recovery from a SAS hard drive failure in a RAID, but the data is still accessible
In a RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 array, if a hard drive fails, the system will enter degraded mode, while the data in it is still accessible. In this case, RAID rebuild allows you to retrieve files from the remaining drives to rebuild the lost data. To avoid data loss during RAID rebuild, follow these recommendations:
- Do not save or delete files on the RAID.
- Do not install any software on the RAID.
- Do not run CHKDSK or other file system tools to repair the RAID, as they may modify file system metadata and cause irreversible data loss.
After understanding these suggestions, you can start rebuilding the RAID.
Step 1: Select a new hard drive. Select a new hard drive with the same or higher specifications (capacity, interface type) as the failed hard drive.
Step 2: Insert the new hard drive to replace the failed one. When replacing, you need to make sure the power is off to avoid incorrect operation. In systems that support hot-swap, you can directly insert the new hard drive.
Step 3: Rebuild the RAID. After that, RAID will rebuild itself. And the system will recover the lost part from the redundant data and synchronize it to the new hard drive.
Scenario 2. Data recovery from file system damage, RAID configuration loss, or human error
If the data is lost due to file system damage, RAID configuration loss, or human error, it is best to use data recovery software to get it back. MiniTool Power Data Recovery Free is a powerful RAID data recovery software, which can be used to recover data from SAS hard drive. The main reasons include:
- Support for multiple storage devices: MiniTool Power Data Recovery can scan and recover files from multiple storage devices such as hard drives, RAID arrays, SSDs, etc.
- Support for multiple file types: This powerful tool supports the recovery of multiple file types, including documents, pictures, videos, audio, etc., to meet the needs of different users.
- Powerful scanning function: It can deeply scan the hard drive to identify lost partitions and file systems, which is suitable for situations where the RAID configuration is lost or the file system is damaged.
- Intuitive interface: MiniTool provides an intuitive interface suitable for all users. Whether you are a beginner or a professional, you can quickly find the needed functions.
- Strong compatibility: It is strongly compatible with Windows 11/10/8/8.1. For most users, it can be used directly.
Besides these, this tool has many editions to meet the needs of different users. The free edition supports recovering 1 GB of files without charge. Download and install it on your device to do a SAS hard drive data recovery.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Insert your SAS hard drive, and then launch the MiniTool Power Data Recovery software. After loading the disk information, you will enter the Logical Drives section of the main interface, where all the partitions are displayed. Find the partition, hover your cursor on the section, and click on Scan to scan for data. Alternatively, you can switch to the Devices tab, where all the disks are listed, select the disk, and click on Scan to start scanning.
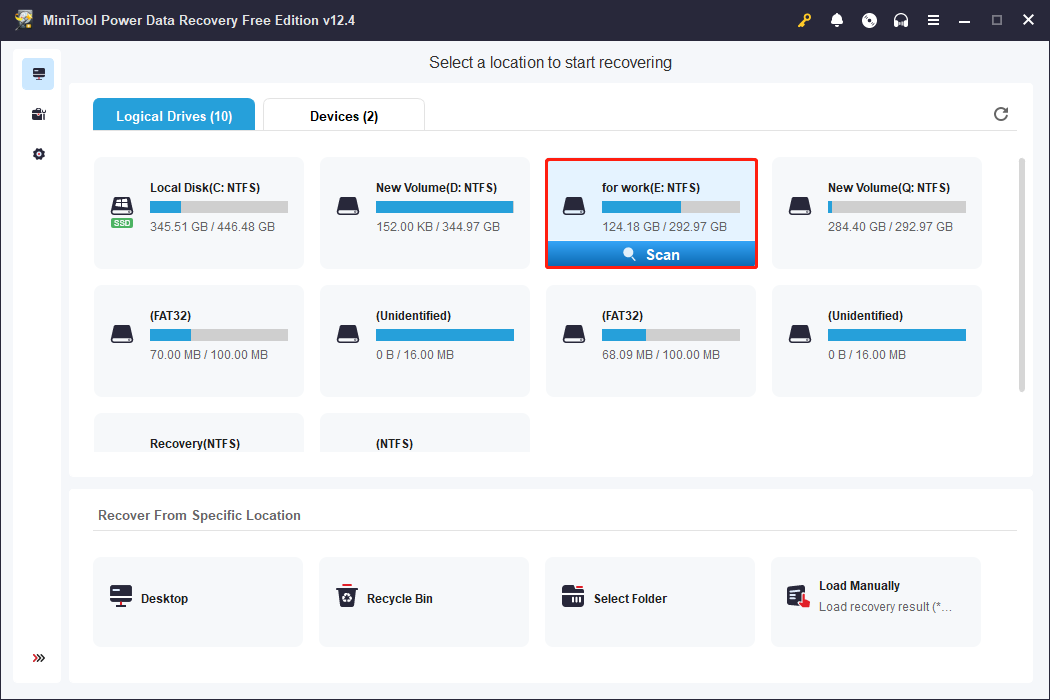
Step 2: The scanning process may take some time. For the best results, you are advised to wait patiently for the process to be completed. When it ends, in accordance with the original file path, they are generally classified into three folders under the Path tab, including Deleted Files, Lost Files, and Existing Files. If you want to find files according to file structures, expand the folder to locate them. Of course, there is more than one way to find files. Let me introduce you to more ways to help you find the files more personally.
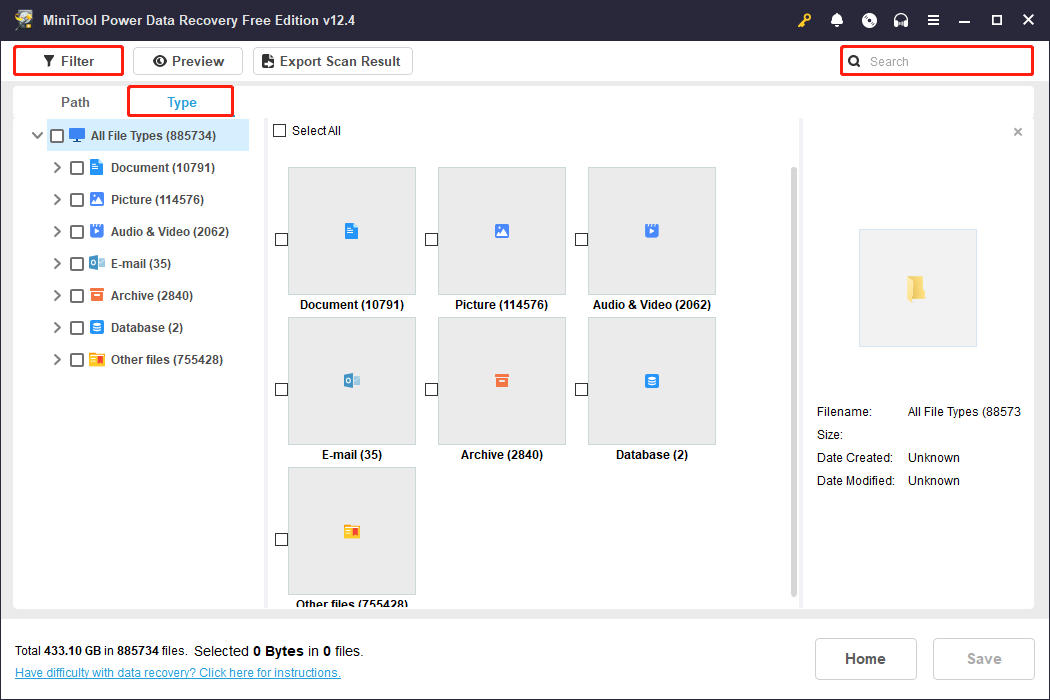
- Type: Under the Type tab, files are sorted based on the file types and formats, including documents, pictures, audio, videos, and more. If you want to recover a certain type of file, this feature can help you save more time.
- Filter: This feature provides diverse filter criteria, including file type, file size, date modified, and file category. Click on the Filter button to set filter conditions at once to narrow down the file list.
- Search: This feature allows you to search for the target files by their full or partial file names. Type the file name in the search box and press Enter. All files that do not meet the criteria will be screened out.
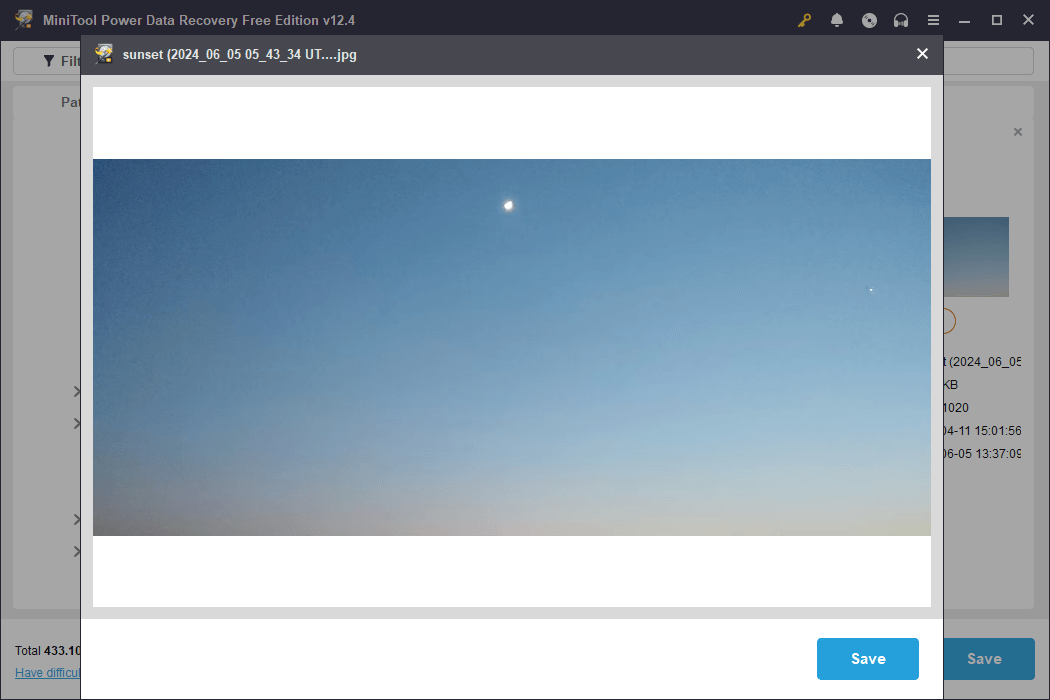
Step 3: Since the free edition only provides 1 GB of free file recovery capacity, it is best to check the file content before recovery to guarantee the accuracy. Select the file and click on the Preview button, or just double-click on the file. The content of the file will show up on the screen. After confirming, close the preview.
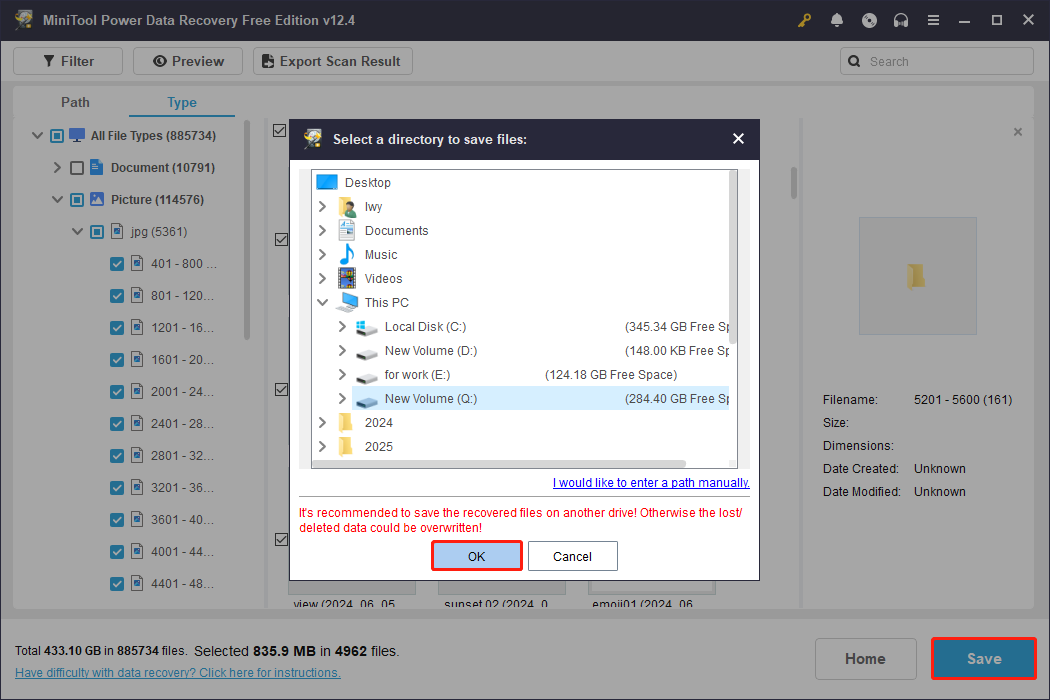
Step 4: Now you can do the last step. Tick all target files and click on the Save button. A window that prompts you to select a storage location will pop up. You need to select a new place instead of the original one to prevent files from being overwritten. Finally, click on the OK button to start saving.
When the Recovery Complete window appears, close the software and check if files have been recovered to the new location.
How to Avoid SAS Hard Drive Data Loss
After a successful recovery, one thing you need to do is take some measures to protect your data from future loss. The following measures can significantly reduce the risk of data loss.
- Avoid physical damage. Make sure to keep the SAS hard drive in a dry place at ordinary times. Avoid excessive temperature and sudden power outages during use.
- Back up regularly. Regularly back up important data to a separate storage device or cloud.
- Monitor drive health. Use SMART tools or the monitoring function of the RAID controller to regularly check the health of the drives.
- Manage RAID arrays carefully. Avoid frequent RAID array rebuilds or configuration changes.
- Protect against viruses and malware. Install reliable antivirus software and scan the system regularly.
Verdict
Although data loss on SAS hard drives in RAID arrays is a headache, it is not hopeless. With correct diagnosis, appropriate tools such as MiniTool Power Data Recovery, and professional operation, data can be successfully recovered in most cases.
More importantly, regularly backing up data and ensuring the smooth operation of storage devices can effectively reduce the risk of data loss.
Hope this article is helpful to you. If you encounter any problems when using MiniTool products, you can send us an email via [email protected].


User Comments :