Windows Command Processor High Memory Usage
The Windows Command Processor (cmd.exe) process is mainly used to perform various tasks and usually does not occupy an abnormally large amount of memory resources while running. If you encounter CMD high memory usage, it typically indicates that the computer may be infected by malware, there could be issues with system settings, or abnormal background processes are interfering with cmd.exe.
When cmd.exe occupies a large amount of memory, the computer may run slowly or even encounter a blue screen of death or a black screen. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to reduce Windows Command Processor high memory usage. Listed below are some useful solutions.
How to Fix if Windows Command Processor Takes up a Lot of RAM
Fix 1. Run a Virus Scan
Some malware may disguise itself as the cmd.exe process to perform malicious activities and cause high memory usage. In this case, you can use Windows Defender to perform a full virus or malware scan, which scans the system files, programs, temporary files, etc. Once a threat is detected, Windows Defender will quarantine or remove them.
Step 1. Press the Windows + I key combination to open Settings.
Step 2. Navigate to Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus and threat protection.
Step 3. Click Scan options.
Step 4. Select Full scan or another preferred scan method, and then click Scan now.
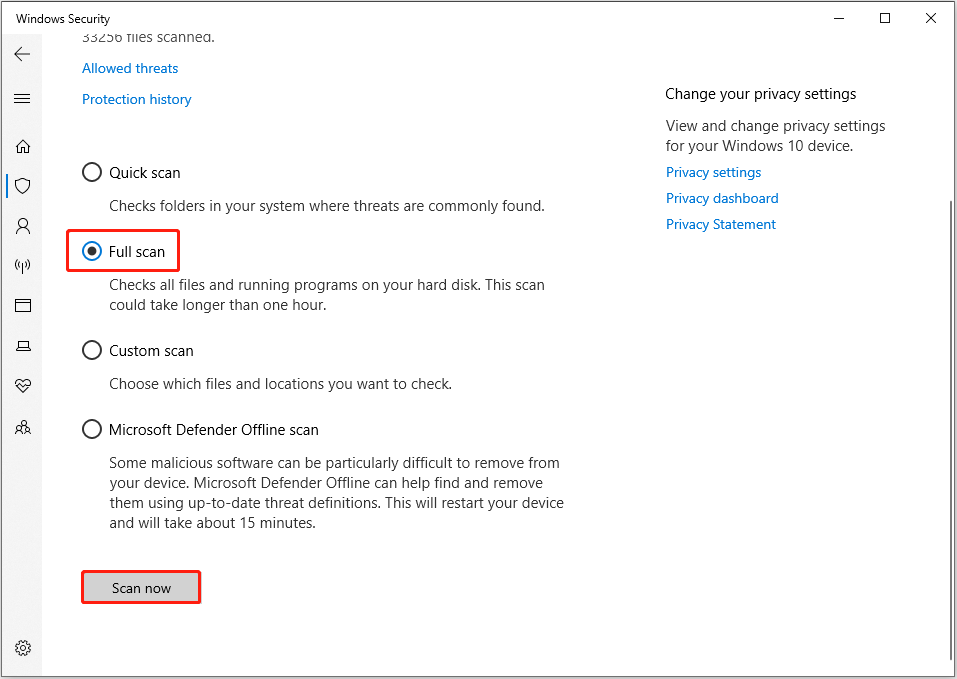
If you uninstalled Windows Defender, you can also run a virus scan by using other third-party antivirus software installed on your computer.
Fix 2. Disable Unnecessary Startup Files
Sometimes, the high memory usage of cmd.exe is caused by certain startup items, especially if you use some automation scripts or task scheduling tools. In this case, you need to disable all unnecessary startup items and check if the problem can be fixed.
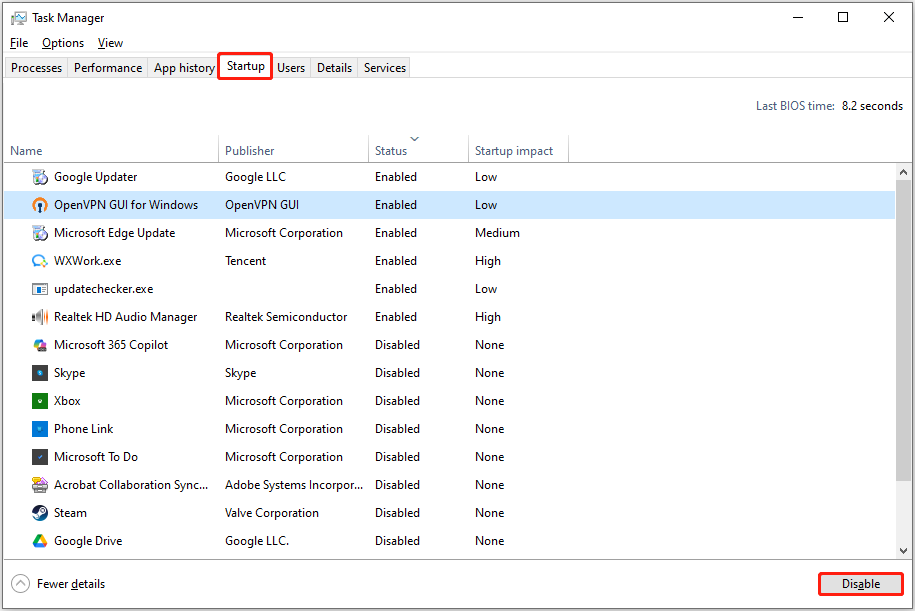
First, right-click the Windows logo button and open Task Manager.
Second, go to the Startup tab, select the unnecessary program that is enabled, and then click Disable. Duplicate this process to disable all targeted items.
Fix 3. Perform a SFC Scan
Corrupted or missing system files can also be the culprit of the Windows Command Processor high memory usage. You can use the SFC command to verify if there are damaged system files and repair or replace them.
- Input cmd in the Windows search box. When the Command Prompt option shows up, right-click it and choose Run as administrator.
- If the User Account Control window prompts, select Yes to continue.
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
Fix 4. Reinstall Windows
Reinstalling Windows can help completely remove potential malware, replace system files, and remove suspicious programs. However, it requires you to reconfigure the system, install applications, restore files, etc. So, it is not recommended to perform a system reinstall unless all of the methods above fail to work.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
To reinstall Windows:
- Download the Windows Media Creation Tool and use it to create a Windows installation USB media.
- Enter BIOS and select USB drive as the preferred boot option.
- Boot from the USB drive, and then start the installation process. Once the installation is complete and the operating system is set up, you can restore your backup files to the new system.
Fix 5. End the Task on Every Startup
Manually ending the task of the Windows Command Processor that takes up a lot of memory from Task Manager every time is not the most thorough solution. However, if the methods listed above do not work for you or you do not want to spend time and effort to reinstall the system, then this is also a temporary executable solution.
MiniTool System Booster TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Bottom Line
Windows Command Processor high memory usage can be fixed by performing a virus scan if it is caused by malware infection. Also, disabling unnecessary startup items, repairing system files, and reinstalling Windows are effective solutions to this problem.

User Comments :